Kindlin-2 enhances c-Myc translation through association with DDX3X to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression
- PMID: 37649609
- PMCID: PMC10465218
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.85421
Kindlin-2 enhances c-Myc translation through association with DDX3X to promote pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression
Abstract
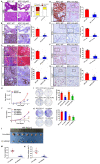
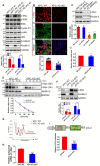
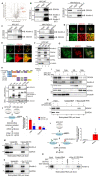
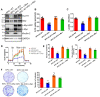
Rationale: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is an aggressive solid tumor, with extremely low survival rates. Identifying key signaling pathways driving PDAC progression is crucial for the development of therapies to improve patient response rates. Kindlin-2, a multi-functional protein, is involved in numerous biological processes including cell proliferation, apoptosis and migration. However, little is known about the functions of Kindlin-2 in pancreatic cancer progression in vivo. Methods: In this study, we employ an in vivo PDAC mouse model to directly investigate the role of Kindlin-2 in PDAC progression. Then, we utilized RNA-sequencing, the molecular and cellular assays to determine the molecular mechanisms by which Kindlin-2 promotes PDAC progression. Results: We show that loss of Kindlin-2 markedly inhibits KrasG12D-driven pancreatic cancer progression in vivo as well as in vitro. Furthermore, we provide new mechanistic insight into how Kindlin-2 functions in this process, A fraction of Kindlin-2 was localized to the endoplasmic reticulum and associated with the RNA helicase DDX3X, a key regulator of mRNA translation. Loss of Kindlin-2 blocked DDX3X from binding to the 5'-untranslated region of c-Myc and inhibited DDX3X-mediated c-Myc translation, leading to reduced c-Myc-mediated glucose metabolism and tumor growth. Importantly, restoration of the expression of either the full-length Kindlin-2 or c-Myc, but not that of a DDX3X-binding-defective mutant of Kindlin-2, in Kindlin-2 deficient PDAC cells, reversed the inhibition of glycolysis and pancreatic cancer progression induced by the loss of Kindlin-2. Conclusion: Our studies reveal a novel Kindlin-2-DDX3X-c-Myc signaling axis in PDAC progression and suggest that inhibition of this signaling axis may provide a promising therapeutic approach to alleviate PDAC progression.
Keywords: DDX3X; Kindlin-2; Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma; c-Myc; translation.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





Similar articles
-
β2-adrenergic receptor signaling promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression through facilitating PCBP2-dependent c-myc expression.Cancer Lett. 2016 Apr 1;373(1):67-76. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.026. Epub 2016 Jan 21. Cancer Lett. 2016. PMID: 26803058
-
Kindlin-2 induced by TGF-β signaling promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma progression through downregulation of transcriptional factor HOXB9.Cancer Lett. 2015 May 28;361(1):75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2015.02.039. Epub 2015 Feb 24. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 25724625
-
Inhibiting NR5A2 targets stemness in pancreatic cancer by disrupting SOX2/MYC signaling and restoring chemosensitivity.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023 Nov 28;42(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s13046-023-02883-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 38012687 Free PMC article.
-
MYC in pancreatic cancer: novel mechanistic insights and their translation into therapeutic strategies.Oncogene. 2016 Mar 31;35(13):1609-18. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.216. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26119937 Review.
-
Oncogenic signaling pathways in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma.Adv Cancer Res. 2023;159:251-283. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2023.02.006. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Adv Cancer Res. 2023. PMID: 37268398 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical functional proteomics of intercellular signalling in pancreatic cancer.Nature. 2025 Jan;637(8046):726-735. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08225-y. Epub 2024 Nov 13. Nature. 2025. PMID: 39537929
-
Targeting DDX3X suppresses progression of KRAS-driven lung cancer by disrupting antioxidative homeostasis and inducing ferroptosis.Cell Death Dis. 2025 Aug 30;16(1):660. doi: 10.1038/s41419-025-07980-8. Cell Death Dis. 2025. PMID: 40885716 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer Statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Qian W, Li J, Chen K, Jiang Z, Cheng L, Zhou C. et al. Metformin suppresses tumor angiogenesis and enhances the chemosensitivity of gemcitabine in a genetically engineered mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Life Sci. 2018;208:253–61. - PubMed
-
- Krebs AM, Mitschke J, Lasierra Losada M, Schmalhofer O, Boerries M, Busch H. et al. The EMT-activator Zeb1 is a key factor for cell plasticity and promotes metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Nat Cell Biol. 2017;19:518–29. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

