Metabolic regulation of endothelial senescence
- PMID: 37649668
- PMCID: PMC10464912
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1232681
Metabolic regulation of endothelial senescence
Abstract
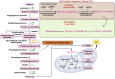
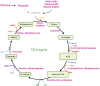
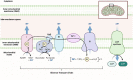
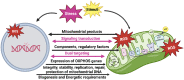
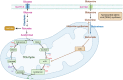
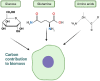
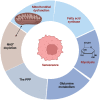
Endothelial cell (EC) senescence is increasingly recognized as a significant contributor to the development of vascular dysfunction and age-related disorders and diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular diseases (CVD). The regulation of cellular senescence is known to be influenced by cellular metabolism. While extensive research has been conducted on the metabolic regulation of senescence in other cells such as cancer cells and fibroblasts, our understanding of the metabolic regulation of EC senescence remains limited. The specific metabolic changes that drive EC senescence are yet to be fully elucidated. The objective of this review is to provide an overview of the intricate interplay between cellular metabolism and senescence, with a particular emphasis on recent advancements in understanding the metabolic changes preceding cellular senescence. I will summarize the current knowledge on the metabolic regulation of EC senescence, aiming to offer insights into the underlying mechanisms and future research directions.
Keywords: SASP; atherosclerosis; cellular metabolism; cellular senescence; endothelial cells.
© 2023 Le.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Divergent mechanisms of metabolic dysfunction drive fibroblast and T-cell senescence.Ageing Res Rev. 2018 Nov;47:24-30. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2018.06.001. Epub 2018 Jun 15. Ageing Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29902528
-
Endothelial Cell Senescence Exacerbates Pulmonary Fibrosis Potentially Through Accelerated Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition.Kobe J Med Sci. 2021 Nov 2;67(3):E84-E91. Kobe J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 35367994 Free PMC article.
-
Senescence mechanisms and targets in the heart.Cardiovasc Res. 2022 Mar 25;118(5):1173-1187. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvab161. Cardiovasc Res. 2022. PMID: 33963378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Premature senescence and cardiovascular disease following cancer treatments: mechanistic insights.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Sep 14;10:1212174. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1212174. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37781317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Endothelial Cell Senescence.Cells. 2022 Mar 31;11(7):1185. doi: 10.3390/cells11071185. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35406749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
New Dawn for Atherosclerosis: Vascular Endothelial Cell Senescence and Death.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 13;24(20):15160. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015160. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In Vitro Modeling of Vascular Senescence.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2906:271-279. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4426-3_16. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40082362
-
Chaperone-mediated autophagy directs a dual mechanism to balance premature senescence and senolysis to prevent intervertebral disc degeneration.Bone Res. 2025 Jun 12;13(1):62. doi: 10.1038/s41413-025-00441-0. Bone Res. 2025. PMID: 40506462 Free PMC article.
-
Endothelial Cell Senescence in Marfan Syndrome: Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Potential of TGF-β Pathway Inhibition.J Am Heart Assoc. 2025 May 6;14(9):e037826. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.124.037826. Epub 2025 Apr 16. J Am Heart Assoc. 2025. PMID: 40240926 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

