Burns Depression Scale Today (BDST): A validation study of BDST against the reference standard of PHQ-9
- PMID: 37649750
- PMCID: PMC10465026
- DOI: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_9_23
Burns Depression Scale Today (BDST): A validation study of BDST against the reference standard of PHQ-9
Abstract
Background: Case finding for low mood is essential in primary care, but it is time-consuming using current depression inventories. The Burns Depression Scale Today (BDST) is a short, simple inventory which assesses mood for today, and we aimed to validate it in this study.
Materials and methods: Consecutive patients with emotional distress seen in a single primary care clinic by one of the authors over 22 months were eligible for this retrospective audit (N = 160). Multiple visits (N = 421) from the same patient were included in the study. The index test was BDST, which assesses the patient's mood for today. The reference standard was the 9-item Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9), which assesses mood over the past 2 weeks. PHQ-9 had a cut-off point of ≥10 and BDST had a cut-off point of ≥6 for a significant mood issue.
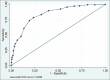
Results: The median age of patients was 35 years, and 63% of the cohort were women. The median BDST score was 8, indicative of moderately low mood, and the median PHQ-9 score was 15, indicative of moderately severe depression. For patients with a BDST score ≥6, the likelihood ratio of a positive test was 2.67. The sensitivity was 85% (95% confidence interval [CI]: 89%-96%) and the specificity was 68% (95% CI: 60%-76%). The area under the curve was 84% (95% CI: 80%-87%).
Conclusion: This audit validates BDST against PHQ-9 and finds it an excellent case-finding tool compared to PHQ-9. This is the first validation study of BDST.
Keywords: Case finding; depression; primary care; sensitivity; specificity; validate.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders Global Health Estimates. Geneva, Switzerland: WHO Document Production Services; 2017. Available from:https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/254610/W?sequence=1 .
-
- Malhi GS, Bell E, Boyce P, Bassett D, Berk M, Bryant RR, et al. The 2020 Royal Australian and New Zealand College of psychiatrists clinical practice guidelines for mood disorders:Bipolar disorder summary. Bipolar Disord. 2020;22:805–21. - PubMed
-
- El-Den S, Chen TF, Gan Y-L, Wong E, O'Reilly CL. The psychometric properties of depression screening tools in primary healthcare settings:A systematic review. J Affect Disorder. 2018;225:503–22. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous