Penetration and durability of CPP-ACP paste and sodium fluoride varnish as desensitizing agents: An in vitro comparison
- PMID: 37649823
- PMCID: PMC10462472
- DOI: 10.34172/joddd.2023.28050
Penetration and durability of CPP-ACP paste and sodium fluoride varnish as desensitizing agents: An in vitro comparison
Abstract
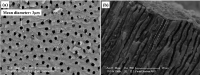
Background: This study aimed to investigate and compare the penetration and durability of two dentin desensitizers, sodium fluoride varnish and casein phosphopeptide-amorphous calcium phosphate (CPP-ACP) paste, using electron microscopy.
Methods: The study was performed on 60 dentin specimens prepared from extracted human premolars. After applying 17% EDTA to remove the smear layer, the specimens were divided into two groups. MI Paste and Bi-fluoride varnish were applied to the specimens. Microscopic images of 20 samples were obtained immediately. Twenty other samples were accessed after 15 days, and the other 20 were accessed after 30 days of toothbrushing and thermal cycling. Both surface and longitudinal cross-sectional images (after sample fracture) were studied. Data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA and Mann-Whitney U test at a significance level of P<0.05.
Results: The mean depth of material penetration was significantly time-dependent and fluctuated in both groups. There was a significant difference between the mean level of plugs between 0, 15, and 30 days (P<0.001). Penetration increased with time for the MI Paste group, while in the Bi-fluoride group, the increase was significant at 15 and 30 days than immediately after application. The mean thickness of the plugs was significantly different at the three time periods, and MI Paste showed a sudden decrease in plug thickness after 15 days.
Conclusion: Immediately after application, Bi-fluoride occluded dentinal tubules more effectively, and its durability after abrasion and thermal fatigue were higher than MI Paste.
Keywords: Dentin; Durability; Fluoride varnish; Scanning electron microscopy; Sensitivity.
©2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests with regards to authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources