Advances in the roles of glycyrrhizic acid in cancer therapy
- PMID: 37649893
- PMCID: PMC10463042
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1265172
Advances in the roles of glycyrrhizic acid in cancer therapy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Advances in the roles of glycyrrhizic acid in cancer therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Dec 14;14:1345663. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1345663. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 38155900 Free PMC article.
Abstract
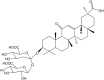
Since the first 70 years of reporting cancer chemotherapy, malignant tumors have been the second most common cause of death in children and adults. Currently, the commonly used anti-cancer methods include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy. Although these treatment methods could alleviate cancer, they lead to different forms of side effects and have no particularly significant effect on prolonging the patients' life span. Glycyrrhizic acid (GL), a native Chinese herbal extract, has a wide range of pharmacological effects, such as anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and immune regulation. In this review, the anti-cancer effects and mechanisms of GL are summarized in various cancers. The inhibition of GL on chemotherapy-induced side effects, including hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, genotoxicity, neurotoxicity and pulmonary toxicity, is highlighted. Therefore, GL may be a promising and ideal drug for cancer therapy.
Keywords: anti-cancer; cancer; glycyrrhizic acid; mechanisms; side effects.
Copyright © 2023 Zhang, Sheng, Xiao, Li, Huang, Jia, Zeng and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Afkhami-Poostchi A., Mashreghi M., Iranshahi M., Matin M. M. (2020). Use of a genetically engineered E. coli overexpressing ÿ-glucuronidase accompanied by glycyrrhizic acid, a natural and anti-inflammatory agent, for directed treatment of colon carcinoma in a mouse model. Int. J. Pharm. 579, 119159. 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2020.119159 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

