The Important Role of Interleukin-2 in COVID-19
- PMID: 37649897
- PMCID: PMC10465260
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/7097329
The Important Role of Interleukin-2 in COVID-19
Abstract
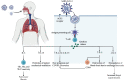
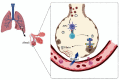
There is controversial literature about the effects of the interleukin-2 (IL-2) cytokine family in COVID-19 pathogenesis and immunity. So we aimed to identify the potential in the role of the IL-2 family in COVID-19. A narrative review search was done through online databases, including PubMed, Scopus, and Web of Science. The search deadline was up to December 2022. We applied no time limits for the searching strategy. After retrieving articles from the databases, the authors summarized the data into two data extraction tables. The first data extraction table described the changes in the IL-2 cytokine family in COVID-19 and the second table described the therapeutic interventions targeting IL-2 family cytokines. The results of the literature on the role of the IL-2 cytokine family do not show a singular rule. IL-2 cytokine family can change during severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. Some studies suggest that IL-2 cytokine family rise during the infection and cause severe inflammatory response and cytokine storm. These cytokines are shown to be increased in immunocompromised patients and worsen their prognosis. In individuals without underlying disease, the upregulation of the IL-2 family shows the clinical outcome of the disease and rises with disease severity. However, some other studies show that these cytokines do not significantly change. IL-2 cytokine family is mostly upregulated in healthy individuals who had vaccination, but immunocompromised patients did not show significant changes after a single dose of vaccines, which shows that these patients need booster doses for efficient immunity. IL-2 cytokine family can also be used as immunotherapy agents in COVID-19.
Copyright © 2023 Leila Ghanbari Naeini et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coronavirus-19 (SARS-CoV-2) induces acute severe lung inflammation via IL-1 causing cytokine storm in COVID-19: a promising inhibitory strategy.J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020 Nov-Dec;34(6):1971-1975. doi: 10.23812/20-1-E. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 2020. PMID: 33016027
-
Tocilizumab in SARS-CoV-2 Patients with the Syndrome of Cytokine Storm: A Narrative Review.Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021;16(2):138-145. doi: 10.2174/1574887115666200917110954. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 2021. PMID: 32940187 Review.
-
The Role of Inflammatory Cytokines (Interleukin-1 and Interleukin-6) as a Potential Biomarker in the Different Stages of COVID-19 (Mild, Severe, and Critical).J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023 Apr;43(4):147-163. doi: 10.1089/jir.2022.0185. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023. PMID: 37062817 Review.
-
Cytokine Storm in Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Adult-Onset Still's Disease: Similarities and Differences.Front Immunol. 2021 Jan 19;11:603389. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.603389. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33552062 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological mechanism of immunomodulatory agents for the treatment of severe cases of COVID-19 infection.Inflamm Res. 2021 Apr;70(4):389-405. doi: 10.1007/s00011-021-01445-2. Epub 2021 Feb 19. Inflamm Res. 2021. PMID: 33608746 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of the Effect of mRNA and Inactivated SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines on the Levels of Cytokines IL-2, IFN-γ, and Anti-RBD Spike SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in People Living with HIV (PLHIV).Biomedicines. 2024 Sep 18;12(9):2115. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12092115. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39335628 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and immunological comparison of COVID-19 disease between critical and non-critical courses: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 16;15:1341168. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1341168. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38690274 Free PMC article.
-
A Case Report of Systemic Capillary Leak Syndrome: When More Than One Inciting Factor Exists, the Question Is Who Pulls the Trigger?Cureus. 2025 Jan 10;17(1):e77261. doi: 10.7759/cureus.77261. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39931582 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory effect of IFN-γ licensed adipose-mesenchymal stromal cells in an in vitro model of inflammation generated by SARS-CoV-2 antigens.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 16;14(1):24235. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75776-5. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39415027 Free PMC article.
-
ULV: A robust statistical method for clustered data, with applications to multi-subject, single-cell omics data.ArXiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 10:arXiv:2406.06767v1. ArXiv. 2024. PMID: 38947924 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

