Sex- and age-dependent contribution of System xc- to cognitive, sensory, and social behaviors revealed by comprehensive behavioral analyses of System xc- null mice
- PMID: 37649973
- PMCID: PMC10462982
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1238349
Sex- and age-dependent contribution of System xc- to cognitive, sensory, and social behaviors revealed by comprehensive behavioral analyses of System xc- null mice
Abstract
Background: System xc- (Sxc-) is an important heteromeric amino acid cystine/glutamate exchanger that plays a pivotal role in the CNS by importing cystine into cells while exporting glutamate. Although certain behaviors have been identified as altered in Sxc- null mutant mice, our understanding of the comprehensive impact of Sxc- on behavior remains incomplete.
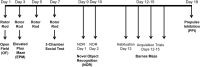
Methods: To address this gap, we compared motor, sensory and social behaviors of male and female mice in mice null for Sxc- (SLC7A11sut/sut) with wildtype littermates (SLC7A11+/+) in a comprehensive and systematic manner to determine effects of genotype, sex, age, and their potential interactions.
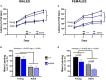
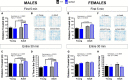
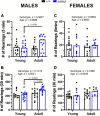
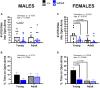
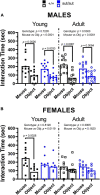
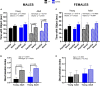
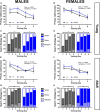
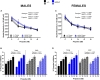
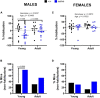
Results: Motor performance was not affected by loss of Sxc- in both males and females, although it was impacted negatively by age. Motor learning was specifically disrupted in female mice lacking Sxc- at both 2 and 6 months of age. Further, female SLC7A11sut/sut mice at both ages exhibited impaired sociability, but normal spatial and recognition memory, as well as sensorimotor gating. Finally, pronounced open-space anxiety was displayed by female SLC7A11sut/sut when they were young. In contrast, young SLC7A11sut/sut male mice demonstrated normal sociability, delayed spatial learning, increased open-space anxiety and heightened sensitivity to noise. As they aged, anxiety and noise sensitivity abated but hyperactivity emerged.
Discussion: We find that the behavioral phenotypes of female SLC7A11sut/sut are similar to those observed in mouse models of autism spectrum disorder, while behaviors of male SLC7A11sut/sut resemble those seen in mouse models of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. These results underscore the need for further investigation of SLC7A11 in neurodevelopment. By expanding our understanding of the potential involvement of Sxc-, we may gain additional insights into the mechanisms underlying complex neurodevelopmental conditions.
Keywords: C3H/HeSnJ; anxiety; attention deficit hyperactivity disorder; autism spectrum disorder; motor function; recognition memory; sensorimotor gating; spatial memory.
Copyright © 2023 Frare, Pitt and Hewett.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyperexcitability and brain morphological differences in mice lacking the cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xc.J Neurosci Res. 2021 Dec;99(12):3339-3353. doi: 10.1002/jnr.24971. Epub 2021 Nov 8. J Neurosci Res. 2021. PMID: 34747522 Free PMC article.
-
Behavioral characterization of system xc- mutant mice.Behav Brain Res. 2014 May 15;265:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Behav Brain Res. 2014. PMID: 24548853
-
The Cystine/Glutamate Antiporter, System xc -, Contributes to Cortical Infarction After Moderate but Not Severe Focal Cerebral Ischemia in Mice.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 May 9;16:821036. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.821036. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35669109 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased epileptogenesis in mice lacking the System xc - transporter occurs in association with a reduction in AMPA receptor subunit GluA1.Epilepsia Open. 2019 Feb 21;4(1):133-143. doi: 10.1002/epi4.12307. eCollection 2019 Mar. Epilepsia Open. 2019. PMID: 30868123 Free PMC article.
-
Glial Glutamate Transporter-Mediated Plasticity: System xc-/xCT/SLC7A11 and EAAT1/2 in Brain Diseases.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023 Mar 20;28(3):57. doi: 10.31083/j.fbl2803057. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023. PMID: 37005761 Review.
References
-
- Baker D. A., Mcfarland K., Lake R. W., Shen H., Tang X. C., Toda S., et al. (2003). Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat. Neurosci. 6 743–749. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

