Sex-specific associations of γ-glutamyltransferase to HDL-cholesterol ratio and the incident risk of cardiovascular disease: three Korean longitudinal cohorts from different regions
- PMID: 37649976
- PMCID: PMC10464609
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1231502
Sex-specific associations of γ-glutamyltransferase to HDL-cholesterol ratio and the incident risk of cardiovascular disease: three Korean longitudinal cohorts from different regions
Abstract
Background: The combination of gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) (GGT/HDL-C) is a novel noninsulin-based marker for assessing the risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus. However, whether the GGT/HDL-C ratio is related to the risk of incident cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk is not well known. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the longitudinal effect of GGT/HDL-C ratio on incident CVD risk in three large cohorts of Korean men and women.
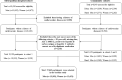
Methods: Data were assessed from 27,643 participants without CVD from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KoGES), Health Risk Assessment Study (HERAS), and Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) (HERAS-HIRA) datasets. The participants were divided into four groups according to the GGT/HDL-C quartiles. We prospectively assessed hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for CVD using multivariate Cox proportional-hazard regression models over a 50-month period following the baseline survey.
Results: During the follow-up period, 949 patients (3.4%; 529 men and 420 women) developed CVD. The HRs of CVD for GGT/HDL-C quartiles 2-4 were 1.36 (95% CI, 0.91-2.02), 1.54 (95% CI, 1.05-2.26), and 1.66 (95% CI, 1.12-2.47) after adjusting for metabolic parameters in women, but GGT/HDL-C did not show a trend toward increases in incident CVD in men. Regional discrepancies were evident in the results; the increase in HR in the metropolitan hospital cohort was more pronounced than that in the urban cohort, and the risk was not increased in the rural cohort.
Conclusion: GGT/HDL-C ratio may be a useful predictive marker for CVD in women. Furthermore, the prevalence of CVD was strongly correlated with the GGT/HDL-C ratio in metropolitan areas, and this correlation was more significant than that observed with GGT or HDL-C in isolation.
Keywords: GGT/HDL-C ratio; cardiovascular disease; cohort study; regional discrepancies; sex difference.
Copyright © 2023 Jung, Park, Ryu and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Roth GA, Abate D, Abate KH, Abay SM, Abbafati C, Abbasi N, et al. Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet (2018) 392(10159):1736–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous