Statistical Challenges When Analyzing SARS-CoV-2 RNA Measurements Below the Assay Limit of Quantification in COVID-19 Clinical Trials
- PMID: 37650235
- PMCID: PMC10469328
- DOI: 10.1093/infdis/jiad285
Statistical Challenges When Analyzing SARS-CoV-2 RNA Measurements Below the Assay Limit of Quantification in COVID-19 Clinical Trials
Abstract
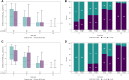
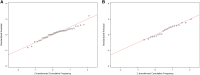
Most clinical trials evaluating coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) therapeutics include assessments of antiviral activity. In recently completed outpatient trials, changes in nasal severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RNA levels from baseline were commonly assessed using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) or mixed models for repeated measures (MMRM) with single imputation for results below assay lower limits of quantification (LLoQ). Analyzing changes in viral RNA levels with singly imputed values can lead to biased estimates of treatment effects. In this article, using an illustrative example from the ACTIV-2 trial, we highlight potential pitfalls of imputation when using ANCOVA or MMRM methods, and illustrate how these methods can be used when considering values <LLoQ as censored measurements. Best practices when analyzing quantitative viral RNA data should include details about the assay and its LLoQ, completeness summaries of viral RNA data, and outcomes among participants with baseline viral RNA ≥ LLoQ, as well as those with viral RNA < LLoQ. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04518410.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2 RNA; linear regression for censored data; randomized trial.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. C. B. M. participated on a data safety monitoring board for the BONE STAR study. K. W. C. has received research funding to the institution from Merck Sharp & Dohme; and is a consultant for Pardes Biosciences. J. Z. L. has consulted for Abbvie; and received research support from Merck. A. L. G. reports contract testing from Abbott, Cepheid, Novavax, Pfizer, Janssen, and Hologic; and research support from Gilead. R. B. I. received consulting fees from SeaGen and Resverlogix unrelated to this work; and research funding through her institution from Novartis and Ascentage Pharma Group. E. S. D. receives consulting fees from Gilead Sciences, Merck, and GSK/ViiV; and research support through the institution from Gilead Sciences and GSK/ViiV. D. A. W. has received funding to the institution to support research; and honoraria for advisory boards and consulting from Gilead Sciences. J. S. C. has consulted for Merck and Company. J. J. E. is an ad hoc consultant to GSK/VIR; and data monitoring committee chair for Adagio phase 3 studies. D. M. S. has consulted for Evidera, Fluxergy, Kiadis, Linear Therapies, Matrix BioMed, Arena Pharmaceuticals, VxBiosciences, Model Medicines, Bayer Pharmaceuticals, Signant Health, and Brio Clinical. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures
Update of
-
Statistical Challenges when Analyzing SARS-CoV-2 RNA Measurements Below the Assay Limit of Quantification in COVID-19 Clinical Trials.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 17:2023.03.13.23287208. doi: 10.1101/2023.03.13.23287208. medRxiv. 2023. Update in: J Infect Dis. 2023 Aug 31;228(Suppl 2):S101-S110. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad285. PMID: 36993419 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. COVID-19: developing drugs and biological products for treatment or prevention [Internet]. 2021. https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents.... Accessed 30 October 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- UM1 AI069423/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI106701/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069424/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/NH/NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI069463/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069432/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI069412/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068634/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI068636/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

