Nicotinamide riboside intervention alleviates hematopoietic system injury of ionizing radiation-induced premature aging mice
- PMID: 37650560
- PMCID: PMC10652312
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.13976
Nicotinamide riboside intervention alleviates hematopoietic system injury of ionizing radiation-induced premature aging mice
Abstract
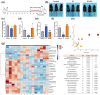
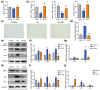
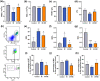
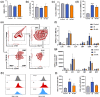
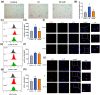
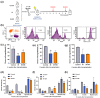
Radiotherapy destroys cancer cells and inevitably harms normal human tissues, causing delayed effects of acute radiation exposure (DEARE) and accelerating the aging process in most survivors. However, effective methods for preventing premature aging induced by ionizing radiation are lacking. In this study, the premature aging mice of DEARE model was established after 6 Gy total body irradiation (TBI). Then the therapeutic effects and mechanism of nicotinamide riboside on the premature aging mice were evaluated. The results showed that 6 Gy TBI induced premature aging of the hematopoietic system in mice. Nicotinamide riboside treatment reversed aging spleen phenotypes by inhibiting cellular senescence and ameliorated serum metabolism profiles. Further results demonstrated that nicotinamide riboside supplementation alleviated the myeloid bias of hematopoietic stem cells and temporarily restored the regenerative capacity of hematopoietic stem cells probably by mitigating the reactive oxygen species activated GCN2/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathway. The results of this study firstly indicate that nicotinamide riboside shows potential as a DEARE therapeutic agent for radiation-exposed populations and patients who received radiotherapy.
Keywords: cellular senescence; ionizing radiation; nicotinamide riboside; radiotherapy.
© 2023 The Authors. Aging Cell published by Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nicotinamide riboside alleviates ionizing radiation-induced intestinal senescence by alleviating oxidative damage and regulating intestinal metabolism.J Adv Res. 2025 Jun;72:421-432. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.07.010. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 39029900 Free PMC article.
-
Time-restricted feeding prevents ionizing radiation-induced hematopoietic stem cell damage by inhibiting NOX-4/ROS/p38 MAPK pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Mar 30;130:111695. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.111695. Epub 2024 Feb 23. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38401461
-
Inhibition of UVB radiation-induced tissue swelling and immune suppression by nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2024 May;40(3):e12961. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12961. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2024. PMID: 38676310 Free PMC article.
-
Rejuvenating Aged Hematopoietic Stem Cells Through Improvement of Mitochondrial Function.Ann Lab Med. 2018 Sep;38(5):395-401. doi: 10.3343/alm.2018.38.5.395. Ann Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 29797808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What is really known about the effects of nicotinamide riboside supplementation in humans.Sci Adv. 2023 Jul 21;9(29):eadi4862. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adi4862. Epub 2023 Jul 21. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37478182 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role and Mechanism of Nicotinamide Riboside in Oxidative Damage and a Fibrosis Model of Trabecular Meshwork Cells.Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024 Mar 1;13(3):24. doi: 10.1167/tvst.13.3.24. Transl Vis Sci Technol. 2024. PMID: 38546981 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Mechanisms in Senescent Cells Induced by Natural Aging and Ionizing Radiation.Cells. 2024 Mar 21;13(6):550. doi: 10.3390/cells13060550. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38534394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitigation of radiation-induced jejunum injuries in rats through modulation of the p53-miR34a axis using etoricoxib-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 10;14(1):23728. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73469-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39390040 Free PMC article.
-
Astragaloside IV accelerates hematopoietic reconstruction by improving the AMPK/PGC1α-mediated mitochondrial function in hematopoietic stem cells.Chin Med. 2025 Apr 1;20(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01092-3. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40170084 Free PMC article.
-
Exercise alleviates hematopoietic stem cell injury following radiation via the carnosine/Slc15a2-p53 axis.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Dec 3;22(1):582. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01959-2. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39627813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Camacho‐Pereira, J. , Tarragó, M. G. , Chini, C. C. S. , Nin, V. , Escande, C. , Warner, G. M. , Puranik, A. S. , Schoon, R. A. , Reid, J. M. , Galina, A. , & Chini, E. N. (2016). CD38 dictates age‐related NAD decline and mitochondrial dysfunction through an SIRT3‐dependent mechanism. Cell Metabolism, 23(6), 1127–1139. 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.05.006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chai, X. , Li, D. , Cao, X. , Zhang, Y. , Mu, J. , Lu, W. , Xiao, X. , Li, C. , Meng, J. , Chen, J. , Li, Q. , Wang, J. , Meng, A. , & Zhao, M. (2015). ROS‐mediated iron overload injures the hematopoiesis of bone marrow by damaging hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells in mice. Scientific Reports, 5, 10181. 10.1038/srep10181 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chalvon‐Demersay, T. , Gaudichon, C. , Moro, J. , Even, P. C. , Khodorova, N. , Piedcoq, J. , Viollet, B. , Averous, J. , Maurin, A. C. , Tome, D. , Foretz, M. , Fafournoux, P. , & Azzout‐Marniche, D. (2023). Role of liver AMPK and GCN2 kinases in the control of postprandial protein metabolism in response to mid‐term high or low protein intake in mice. European Journal of Nutrition, 62(1), 407–417. 10.1007/s00394-022-02983-z - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

