Multimodal deep learning approaches for single-cell multi-omics data integration
- PMID: 37651607
- PMCID: PMC10516349
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbad313
Multimodal deep learning approaches for single-cell multi-omics data integration
Abstract
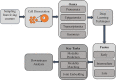
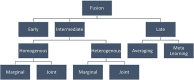
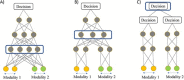
Integrating single-cell multi-omics data is a challenging task that has led to new insights into complex cellular systems. Various computational methods have been proposed to effectively integrate these rapidly accumulating datasets, including deep learning. However, despite the proven success of deep learning in integrating multi-omics data and its better performance over classical computational methods, there has been no systematic study of its application to single-cell multi-omics data integration. To fill this gap, we conducted a literature review to explore the use of multimodal deep learning techniques in single-cell multi-omics data integration, taking into account recent studies from multiple perspectives. Specifically, we first summarized different modalities found in single-cell multi-omics data. We then reviewed current deep learning techniques for processing multimodal data and categorized deep learning-based integration methods for single-cell multi-omics data according to data modality, deep learning architecture, fusion strategy, key tasks and downstream analysis. Finally, we provided insights into using these deep learning models to integrate multi-omics data and better understand single-cell biological mechanisms.
Keywords: data integration; deep learning; multi-omics; single-cell.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Stark R, Grzelak M, Hadfield J. RNA sequencing: the teenage years. Nat Rev Genet 2019;20:631–56. - PubMed
-
- Ramachandram D, Taylor GW. Deep multimodal learning: a survey on recent advances and trends. IEEE Signal Process Mag 2017;34:96–108.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

