Bempegaldesleukin Plus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma: The Open-Label, Phase III PIVOT IO 001 Trial Results
- PMID: 37651676
- PMCID: PMC10602507
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.23.00172
Bempegaldesleukin Plus Nivolumab in Untreated Advanced Melanoma: The Open-Label, Phase III PIVOT IO 001 Trial Results
Abstract
Purpose: Despite marked advances in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, the need for novel therapies remains. Bempegaldesleukin (BEMPEG), a pegylated interleukin-2 (IL-2) cytokine prodrug, demonstrated efficacy in the phase II PIVOT-02 trial. PIVOT IO 001 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03635983) is a phase III, randomized, open-label study that builds on the PIVOT-02 results in first-line melanoma.
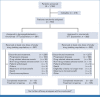
Methods: Patients with previously untreated, unresectable, or metastatic melanoma were randomly assigned 1:1 to receive BEMPEG plus nivolumab (NIVO) or NIVO monotherapy. Primary end points were objective response rate (ORR) and progression-free survival (PFS) by blinded independent central review and overall survival (OS). Secondary and exploratory end points included additional efficacy measures, safety, and pharmacokinetics (PKs) and pharmacodynamics analyses.
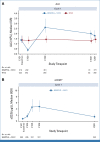
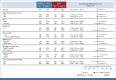
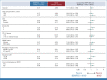
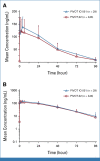
Results: In 783 patients (n = 391, BEMPEG plus NIVO; n = 392, NIVO monotherapy), the median follow-up was 11.6 months in the intent-to-treat population. The ORR with BEMPEG plus NIVO was 27.7% versus 36.0% with NIVO (two-sided P = .0311). The median PFS with BEMPEG plus NIVO was 4.17 months (95% CI, 3.52 to 5.55) versus 4.99 months (95% CI, 4.14 to 7.82) with NIVO (hazard ratio [HR], 1.09; 97% CI, 0.88 to 1.35; P = .3988). The median OS was 29.67 months (95% CI, 22.14 to not reached [NR]) with BEMPEG plus NIVO versus 28.88 months (95% CI, 21.32 to NR) with NIVO (HR, 0.94; 99.929% CI, 0.59 to 1.48; P = .6361). Grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse events (AEs) and serious AE rates were higher with the combination (21.7% and 10.1%, respectively) versus NIVO (11.5% and 5.5%, respectively). BEMPEG PK exposure and absolute lymphocyte count changes after BEMPEG plus NIVO were comparable between PIVOT IO 001 and PIVOT-02.
Conclusion: The PIVOT IO 001 study did not meet its primary end points of ORR, PFS, and OS. Increased toxicity was observed with BEMPEG plus NIVO versus NIVO.
Conflict of interest statement
The following represents disclosure information provided by authors of this manuscript. All relationships are considered compensated unless otherwise noted. Relationships are self-held unless noted. I = Immediate Family Member, Inst = My Institution. Relationships may not relate to the subject matter of this manuscript. For more information about ASCO's conflict of interest policy, please refer to
Open Payments is a public database containing information reported by companies about payments made to US-licensed physicians (
This author is a member of the
No other potential conflicts of interest were reported.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

