Stimulant use, HIV, and immune dysregulation among sexual minority men
- PMID: 37651812
- PMCID: PMC10544798
- DOI: 10.1016/j.drugalcdep.2023.110942
Stimulant use, HIV, and immune dysregulation among sexual minority men
Abstract
Background: Sexual minority men (SMM) report high rates of stimulant use (e.g., crystal methamphetamine, cocaine) and HIV infection. Stimulant use contributes to immune dysfunction, which enhances risk for HIV acquisition and pathogenesis. Research is needed to examine the independent and interactive relationships of stimulant use and HIV infection with systemic immune dysregulation among SMM, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: From 2020-2022, 75 SMM in Miami, Florida with and without HIV completed an online survey and provided biospecimens to assess HIV status and viral load (VL), recent stimulant use, and soluble markers of immune activation and inflammation in plasma, including soluble CD14 (sCD14) and elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP > 1.0mg/L). Sociodemographics and prior SARS-CoV-2 infection were compared across HIV status/stimulant use groups. Moderation models examined the independent and interactive associations of stimulant use and HIV status with sCD14 and elevated hs-CRP.
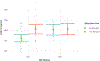
Results: Thirty participants were persons living with HIV (PWH) (50% with stimulant use), and 45 were HIV-negative (44% with stimulant use). SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with stimulant use/HIV groups or immune outcomes. HIV-negative SMM without stimulant use had lower sCD14 compared to other SMM, as well as lower odds of elevated hs-CRP compared to PWH who used stimulants. Stimulant use showed independent associations with immune dysregulation that persisted after controlling for HIV status and VL, whereas HIV status was only independently associated with elevated hs-CRP in one model not controlling for VL.
Conclusions: Among SMM, stimulant use was independently associated with elevated immune activation and inflammation.
Keywords: HIV; High sensitivity C-reactive protein; Inflammation; SCD14; Sexual minority men; Stimulant use.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest No Conflict Declared.
Figures

References
-
- Armah KA, McGinnis K, Baker J, Gibert C, Butt AA, Bryant KJ, Goetz M, Tracy R, Oursler KK, Rimland D, Crothers K, Rodriguez-Barradas M, Crystal S, Gordon A, Kraemer K, Brown S, Gerschenson M, Leaf DA, Deeks SG, … Freiberg M (2012). HIV status, burden of comorbid disease, and biomarkers of inflammation, altered coagulation, and monocyte activation. Clinical Infectious Diseases: An Official Publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America, 55(1), 126–136. 10.1093/cid/cis406 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bassuk SS, Rifai N, & Ridker PM (2004). High-sensitivity C-reactive protein: Clinical importance. Current Problems in Cardiology, 29(8), 439–493. - PubMed
-
- Carrico AW, Cherenack EM, Roach ME, Riley ED, Oni O, Dilworth SE, Shoptaw S, Hunt P, Roy S, Pallikkuth S, & Pahwa S (2018). Substance-Associated Elevations in Monocyte Activation Among Methamphetamine Users with Treated HIV Infection. AIDS (London, England), 32(6), 767–771. 10.1097/QAD.0000000000001751 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

