Flavonoids Quercetin and Kaempferol Are NR4A1 Antagonists and Suppress Endometriosis in Female Mice
- PMID: 37652054
- PMCID: PMC10502789
- DOI: 10.1210/endocr/bqad133
Flavonoids Quercetin and Kaempferol Are NR4A1 Antagonists and Suppress Endometriosis in Female Mice
Abstract
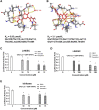
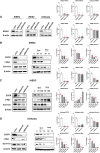
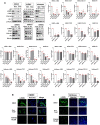
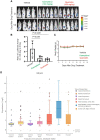
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) plays an important role in endometriosis progression; levels of NR4A1 in endometriotic lesions are higher than in normal endometrium, and substituted bis-indole analogs (NR4A1) antagonists suppress endometriosis progression in mice with endometriosis. In addition, the flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin are natural products that directly bind NR4A1 and significantly repress the intrinsic NR4A1-dependent transcriptional activity in human endometriotic epithelial and stromal cells and Ishikawa endometrial cancer cells. NR4A1 knockdown and inhibition of NR4A1 by kaempferol and quercetin suppressed proliferation of human endometriotic epithelial cells and Ishikawa cells by inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor/c-Myc/survivin-mediated growth-promoting and survival pathways, The mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling and αSMA/CTGF/COL1A1/FN-mediated fibrosis signaling but increasing Thioredoxin domain Containing 5/SESN2-mediated oxidative/estrogen receptors stress signaling. In human endometriotic stromal cells, NR4A1 knockdown and inhibition of NR4A1 by kaempferol and quercetin primarily inhibited mTOR signaling by suppressing proliferation of human endometrial stromal cells. In addition, kaempferol and quercetin treatment also effectively suppressed the growth of endometriotic lesions in mice with endometriosis compared with the vehicle without any body weight changes. Therefore, kaempferol and quercetin are NR4A1 antagonists with potential as nutritional therapy for endometriosis.
Keywords: NR4A1 antagonists; endometriosis; kaempferol; quercetin.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Bis-Indole-Derived Nuclear Receptor 4A1 (NR4A1, Nur77) Ligands as Inhibitors of Endometriosis.Endocrinology. 2020 Apr 1;161(4):bqaa027. doi: 10.1210/endocr/bqaa027. Endocrinology. 2020. PMID: 32099996 Free PMC article.
-
Flavonoids kaempferol and quercetin are nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1, Nur77) ligands and inhibit rhabdomyosarcoma cell and tumor growth.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 14;40(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02199-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34906197 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonists induce ROS-dependent inhibition of mTOR signaling in endometrial cancer.Gynecol Oncol. 2019 Jul;154(1):218-227. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2019.04.678. Epub 2019 Apr 30. Gynecol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31053403 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the Potential: How Flavonoids Affect Angiogenesis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Proliferation, Invasion, and Alter Receptor Interactions in Endometriosis.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 7;13(1):e4607. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4607. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endometriosis and nuclear receptors.Hum Reprod Update. 2019 Jul 1;25(4):473-485. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmz005. Hum Reprod Update. 2019. PMID: 30809650 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Prunin: An Emerging Anticancer Flavonoid.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 16;26(6):2678. doi: 10.3390/ijms26062678. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40141319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Focusing on the role of protein kinase mTOR in endometrial physiology and pathology: insights for therapeutic interventions.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 24;51(1):359. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08937-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38400863 Review.
-
Perfluorooctane Sulfonate (PFOS) and Related Compounds Induce Nuclear Receptor 4A1 (NR4A1)-Dependent Carcinogenesis.Chem Res Toxicol. 2025 Apr 21;38(4):705-716. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.4c00528. Epub 2025 Mar 11. Chem Res Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40066943 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary patterns and nutritional supplementation in the management of endometriosis: a review.Front Nutr. 2025 Mar 12;12:1539665. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1539665. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40144566 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Narrative Review of Quercetin's Role as a Bioactive Compound in Female Reproductive Disorders.Nutrients. 2025 Mar 24;17(7):1118. doi: 10.3390/nu17071118. Nutrients. 2025. PMID: 40218878 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eskenazi B, Warner ML. Epidemiology of endometriosis. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1997;24(2):235‐258. - PubMed
-
- Zondervan KT, Becker CM, Koga K, Missmer SA, Taylor RN, Viganò P. Endometriosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2018;4(1):9. - PubMed
-
- Angioni S, Cofelice V, Pontis A, Tinelli R, Socolov R. New trends of progestins treatment of endometriosis. Gynecol Endocrinol. 2014;30(11):769‐773. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

