Clinicopathological Significance of DUB3 Expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Relationship Between DUB3 Expression and LATS1 Expression
- PMID: 37652526
- PMCID: PMC10500508
- DOI: 10.21873/invivo.13332
Clinicopathological Significance of DUB3 Expression in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and Relationship Between DUB3 Expression and LATS1 Expression
Abstract
Background/aim: Deubiquitinating enzyme 3 (DUB3) is a member of the ubiquitin-specific proteases family involved in regulating cell proliferation, invasion, and apoptosis. However, the biological role and clinicopathological significance of DUB3 expression have not been elucidated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
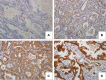
Patients and methods: We evaluated the expression of DUB3 by immunohistochemistry using tissue microarrays and assessed the clinicopathologic significance of DUB3 expression levels in 187 patients with NSCLC, including its two major subtypes (93 cases of adenocarcinoma and 72 cases of squamous cell carcinoma).
Results: In adenocarcinoma, we observed that DUB3 expression had an effect on tumor size (p=0.030), vessel invasion (p=0.038), T stage (p=0.014), and tumor recurrence (p=0.002). Kaplan-Meier curves with log-rank test showed that high DUB3 expression was correlated with significantly more favorable clinical outcomes compared to those of the low expression group in adenocarcinoma (p=0.013). Multivariate analysis of disease-free survival also demonstrated that DUB3 expression is an independent prognostic factor in lung adenocarcinoma (p=0.017). Additionally, we identified the correlation between DUB3 and the expression of large tumor suppressor kinase 1 expression, a core protein of the Hippo pathway.
Conclusion: DUB3 could function as a tumor suppressor by regulating the Hippo pathway in lung adenocarcinoma and can be considered a powerful predictive factor and therapeutic target.
Keywords: Carcinoma; DUB3 protein; LATS1 protein; non-small-cell lung; prognosis.
Copyright © 2023, International Institute of Anticancer Research (Dr. George J. Delinasios), All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- McFarlane C, McFarlane S, Paul I, Arthur K, Scheaff M, Kerr K, Stevenson M, Fennell DA, Johnston JA. The deubiquitinating enzyme USP17 is associated with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) recurrence and metastasis. Oncotarget. 2013;4(10):1836–1843. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.1282. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Braten O, Livneh I, Ziv T, Admon A, Kehat I, Caspi LH, Gonen H, Bercovich B, Godzik A, Jahandideh S, Jaroszewski L, Sommer T, Kwon YT, Guharoy M, Tompa P, Ciechanover A. Numerous proteins with unique characteristics are degraded by the 26S proteasome following monoubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U.S.A. 2016;113(32):E4639–E4647. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1608644113. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
