Developing a framework for the implementation of recommendations for lifestyle factors for people with RMDs across Europe: assessment of current materials and implementation needs
- PMID: 37652556
- PMCID: PMC10476113
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2023-003443
Developing a framework for the implementation of recommendations for lifestyle factors for people with RMDs across Europe: assessment of current materials and implementation needs
Abstract
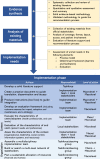
Lifestyle factors (such as diet, physical activity or smoking habits, among others) are known to influence the progression of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs). Despite contemporary improvements in RMD care, the management of lifestyle factors is suboptimal. In the context of a recent European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology (EULAR) task force, existing informative materials regarding lifestyle factors for people with RMDs were collected from national organisations across European countries. Current materials show important limitations in terms of coverage, literature support and access, which may make the implementation of successful interventions difficult. In the present viewpoint, a roadmap to cover these gaps at the European level with the recent EULAR recommendations on lifestyle factors is discussed from an implementation perspective. This analysis may pave the ground for future implementation endeavours at the European level related to non-pharmacological interventions that may also be applicable beyond rheumatology.
Keywords: arthritis, rheumatoid; health services research; nursing; patient care team; qualitative research.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: JG is currently a full-time employee of IQVIA (UK).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Levelling the playing field of RMD research across Europe to address patients' needs: the emerging EULAR Research Centre.RMD Open. 2022 Jun;8(2):e002456. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2022-002456. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 35714997 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of diet on the outcomes of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs): systematic review and meta-analyses informing the 2021 EULAR recommendations for lifestyle improvements in people with RMDs.RMD Open. 2022 Jun;8(2):e002167. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002167. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 35654458 Free PMC article.
-
2021 EULAR recommendations regarding lifestyle behaviours and work participation to prevent progression of rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases.Ann Rheum Dis. 2023 Jan;82(1):48-56. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-222020. Epub 2022 Mar 8. Ann Rheum Dis. 2023. PMID: 35260387 Review.
-
Effects of physical exercise and body weight on disease-specific outcomes of people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases (RMDs): systematic reviews and meta-analyses informing the 2021 EULAR recommendations for lifestyle improvements in people with RMDs.RMD Open. 2022 Mar;8(1):e002168. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2021-002168. RMD Open. 2022. PMID: 35361692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of impact of the COVID-19 pandemic from the perspective of patients with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases in Europe: results from the REUMAVID study (phase 1).RMD Open. 2021 Apr;7(1):e001546. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001546. RMD Open. 2021. PMID: 33827969 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . WHO Europe strategy and action plan for NCDs 2016-2025. 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
