A defect in mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis impairs iron metabolism and causes elevated ceramide levels
- PMID: 37653044
- PMCID: PMC11151872
- DOI: 10.1038/s42255-023-00873-0
A defect in mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis impairs iron metabolism and causes elevated ceramide levels
Abstract
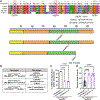
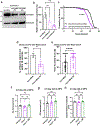
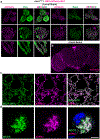
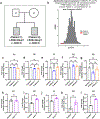
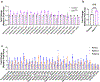
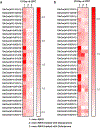
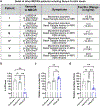
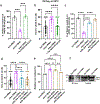
In most eukaryotic cells, fatty acid synthesis (FAS) occurs in the cytoplasm and in mitochondria. However, the relative contribution of mitochondrial FAS (mtFAS) to the cellular lipidome is not well defined. Here we show that loss of function of Drosophila mitochondrial enoyl coenzyme A reductase (Mecr), which is the enzyme required for the last step of mtFAS, causes lethality, while neuronal loss of Mecr leads to progressive neurodegeneration. We observe a defect in Fe-S cluster biogenesis and increased iron levels in flies lacking mecr, leading to elevated ceramide levels. Reducing the levels of either iron or ceramide suppresses the neurodegenerative phenotypes, indicating an interplay between ceramide and iron metabolism. Mutations in human MECR cause pediatric-onset neurodegeneration, and we show that human-derived fibroblasts display similar elevated ceramide levels and impaired iron homeostasis. In summary, this study identifies a role of mecr/MECR in ceramide and iron metabolism, providing a mechanistic link between mtFAS and neurodegeneration.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Figures


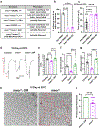
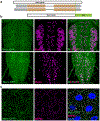
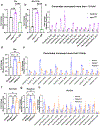
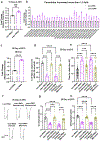
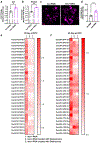
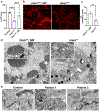
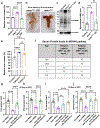
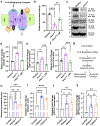
References
-
- Maier T, Jenni S & Ban N Architecture of mammalian fatty acid synthase at 4.5 å resolution. Science 311, 1258–1262 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Miinalainen IJ et al. Characterization of 2-enoyl thioester reductase from mammals. An ortholog of YBR026p/MRF1’p of the yeast mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis type II. J. Biol. Chem 278, 20154–20161 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Nair RR et al. Genetic modifications of Mecr reveal a role for mitochondrial 2-enoyl-CoA/ACP reductase in placental development in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet 26, 2104–2117 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Venkatesan R. et al. Insights into mitochondrial fatty acid synthesis from the structure of heterotetrameric 3-ketoacyl-ACP reductase/3R-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase. Nat. Commun 5, (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

