Establishment of virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system in Luffa acutangula using Phytoene desaturase (PDS) and tendril synthesis related gene (TEN)
- PMID: 37653449
- PMCID: PMC10470258
- DOI: 10.1186/s13007-023-01064-4
Establishment of virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system in Luffa acutangula using Phytoene desaturase (PDS) and tendril synthesis related gene (TEN)
Abstract
Background: Virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) is a reverse genetics technology that can efficiently and rapidly identify plant gene functions. Although a variety of VIGS vectors have been successfully used in plants, only a few reports on VIGS technology in Luffa exist.
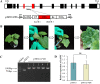
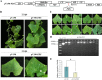
Results: In the present study, a new cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV)-based VIGS vector, pV190, was applied to establish the CGMMV-VIGS to investigate the feasibility of the silencing system for Luffa. Phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene was initially selected as a VIGS marker gene to construct a recombinant vector. Plants infected with Agrobacterium harboring pV190-PDS successfully induced effective silencing in Luffa, and an effective gene silencing phenotype with obvious photobleaching was observed. To further validate the efficiency, we selected TEN for gene-silencing, which encodes a CYC/TB1-like transcription factor and is involved in tendril development. Luffa plants inoculated with the pV190-TEN exhibited shorter tendril length and nodal positions where tendrils appear are higher compared to those of non-inoculated plants. RT-qPCR showed that the expression levels of PDS and TEN were significantly reduced in the CGMMV-VIGS plants. Moreover, we evaluated the CGMMV-VIGS efficiency in three cucurbits, including cucumber, ridge gourd, and bottle gourd.
Conclusion: We successfully established a CGMMV-based VIGS system on ridge gourd and used marker genes to identify the feasibility of the silencing system in Luffa leaves and stems.
Keywords: Cucumber green mottle mosaic virus (CGMMV); Luffa; PDS; TEN; VIGS.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Applications of Virus-Induced Gene Silencing in Cotton.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 17;13(2):272. doi: 10.3390/plants13020272. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A cucumber green mottle mosaic virus vector for virus-induced gene silencing in cucurbit plants.Plant Methods. 2020 Feb 3;16:9. doi: 10.1186/s13007-020-0560-3. eCollection 2020. Plant Methods. 2020. PMID: 32025236 Free PMC article.
-
High rates of virus-induced gene silencing by tobacco rattle virus in Populus.Tree Physiol. 2015 Sep;35(9):1016-29. doi: 10.1093/treephys/tpv064. Epub 2015 Jul 23. Tree Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26209619
-
Delivery of progeny virus from the infectious clone of cucumber green mottle mosaic virus and quantification of the viral load in different host plants.3 Biotech. 2023 Jun;13(6):209. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03630-y. Epub 2023 May 23. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37234077 Free PMC article.
-
Virus-induced gene silencing is a versatile tool for unraveling the functional relevance of multiple abiotic-stress-responsive genes in crop plants.Front Plant Sci. 2014 Jul 8;5:323. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00323. eCollection 2014. Front Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 25071806 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of Virus-Induced Gene Silencing in Cotton.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jan 17;13(2):272. doi: 10.3390/plants13020272. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38256825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hairpin inserts in viral genomes are stable when they conform to the thermodynamic properties of viral RNA substructures.J Virol. 2025 Apr 15;99(4):e0191924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01919-24. Epub 2025 Mar 21. J Virol. 2025. PMID: 40116513 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Analysis of C-Repeat Binding Factor Gene Family in Capsicum baccatum and Functional Exploration in Low-Temperature Response.Plants (Basel). 2024 Feb 17;13(4):549. doi: 10.3390/plants13040549. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38498531 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochrome interacting factor 3 mediates low light signaling to regulate isorhynchophylline biosynthesis in Uncaria rhynchophylla.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 23;14(1):25032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76939-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39443584 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and optimization of a tobacco rattle virus -based virus-induced gene Silencing in Atriplex canescens.Plant Methods. 2025 Aug 7;21(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13007-025-01427-z. Plant Methods. 2025. PMID: 40770802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Van Kammen A. Virus-induced gene silencing in infected and transgenic plants. Trends Plant Sci. 1997;2(11):409–11. doi: 10.1016/S1360-1385(97)01128-X. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

