Research into the mechanism of intervention of Wenjing decoction in endometriosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
- PMID: 37653805
- PMCID: PMC10470684
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034845
Research into the mechanism of intervention of Wenjing decoction in endometriosis based on network pharmacology and molecular docking technology
Abstract
Background: Endometriosis (EMs) is a frequent disease in women and is the principal cause of infertility and dysmenorrhea. Due to its high recurrence rate and serious complications, more research on EMs is needed. We used network pharmacology and molecular docking technology to predict the key active components, targets, and signaling pathways of Wen Jing decoction (WJD) in the treatment of EMs.
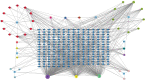
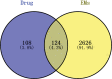
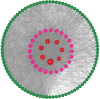
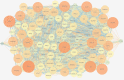
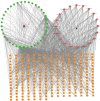
Methods: The components and targets of WJD were collected and identified using the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and BATMAN-TCM. The EMs targets were obtained from GeneCards, OMIM, TTD, Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes (KEGG) and GAD Databases; the Venny diagram was used to analyze the overlap between the targets of WJD and EMs; use Cytoscape 3.8.2 software to build a drug active ingredient-target protein interaction network; after downloading the data from the String online database, Cytoscape 3.8.2 software was used to draw the intersection target protein-protein interaction network diagram. Finally, microbiotic information mapping was used to analyze gene ontology function enrichment and KEGG pathway enrichment. Molecular docking was used to predict the binding affinity of the components of WJD to the targets of EMs.
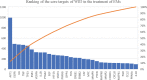
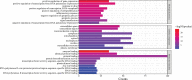
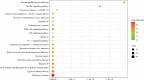
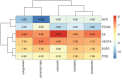
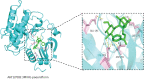
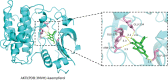
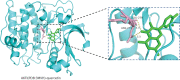
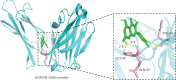
Results: Seventy-eight active ingredients of WJD were screened, corresponding to 108 targets, 2626 EMs-related targets and 124 intersection targets. The results of gene ontology functional enrichment analysis showed that WJD could affect 709 biological processes, 131 molecular functions and 54 cell composition. The enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway yielded 185 pathways. The treatment of EMs by WJD has the characteristics of multiple targets and multiple pathways. Molecular docking with the AutoDock Vina platform found that 5 active ingredients of WJD were successfully docked with 6 common targets.
Conclusion: Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking, WJD was found to act on EMs through multi-targets and related signaling pathways.
Copyright © 2023 the Author(s). Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Mechanism of Shaofu Zhuyu Decoction in treatment of EMT induced dysmenorrhea based on network pharmacology and molecular docking].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021 Dec;46(24):6484-6492. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20210816.401. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34994141 Chinese.
-
Research on the Regulatory Mechanism of Ginseng on the Tumor Microenvironment of Colorectal Cancer based on Network Pharmacology and Bioinformatics Validation.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024;20(5):486-500. doi: 10.2174/1573409919666230607103721. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2024. PMID: 37287284
-
[Exploring the mechanisms of Jujing pill on varicocele-associated male infertility via network pharmacology and molecular docking technology].Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2023 Aug;29(8):688-697. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 2023. PMID: 38619514 Chinese.
-
Exploration of the mechanism of Zisheng Shenqi decoction against gout arthritis using network pharmacology.Comput Biol Chem. 2021 Feb;90:107358. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2020.107358. Epub 2020 Aug 8. Comput Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33243703 Review.
-
Exploring the mechanism of action of Yiyi Fuzi Baijiang powder in colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology and molecular docking studies.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023 Oct;39(2):1107-1127. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2023.2167765. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2023. PMID: 36735641 Review.
Cited by
-
Euodiae Fructus: a review of botany, application, processing, phytochemistry, quality control, pharmacology, and toxicology.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 29;16:1509032. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1509032. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39944619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The mechanism of wen jing tang in the treatment of endometriosis: Insights from network pharmacology and experimental validation.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 17;10(21):e39292. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39292. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524878 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Obstetricians and Gynecologists Branch of Chinese Medical Doctor Association, Endometriosis Assistance Group of Obstetrics and Gynecology Branch of Chinese Medical Association. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis (third edition). Chin J Obstet a Gynecol. 2021;56:812–24.
-
- Yi D, Junji Z, Jinghe L, et al. . Current situation of diagnosis and treatment of endometriosis in 2018 convenient sampling survey report. Chin J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;55:402–7.
-
- Lindsay SF, Luciano DE, Luciano AA. Emerging therapy for endometriosis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2015;20:449–61. - PubMed
-
- Arafah M, Rashid S, Akhtar M. Endometriosis: a comprehensive review. Adv Anat Pathol. 2021;28:30–43. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

