Desmoplastic Ameloblastoma-A Case Report
- PMID: 37654261
- PMCID: PMC10466640
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_44_23
Desmoplastic Ameloblastoma-A Case Report
Abstract
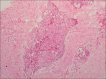
Desmoplastic ameloblastoma (DA) is a rare variant of conventional ameloblastoma. It accounts for only 4%-13% of all ameloblastomas. DA was included in the World Health Organization Classification of Head and Neck Tumors (WHO-2005) as a variant of ameloblastoma with specific clinical, imaging, and histological features. The desmoplastic variant of ameloblastoma usually appears in the anterior and premolar regions as a mixed radiolucent and radiopaque lesion, sometimes resembling a benign fibro-osseous lesion.Ameloblastoma is a locally aggressive tumor that may cause recurrence and in rare cases, malignant transformation with repeated postsurgical recurrences. In this paper, we present a case of a 28-year-old female with swelling in the left upper jaw, a biopsy of which turned out to be DA.
Keywords: Ameloblastoma; benign fibro-osseous lesion; desmoplastic ameloblastoma; odontogenic tumor.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Waldron CA, El-Mofty SK. A histopathologic study of 116 ameloblastomas with special reference to the desmoplastic variant. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987;63:441–51. - PubMed
-
- Sun ZJ, Wu YR, Cheng N, Zwahlen RA, Zhao YF. Desmoplastic ameloblastoma–A review. Oral Oncol. 2009;45:752–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology. 2009.01.016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Huang CM, Chen JY, Chen CH, Huang CJ. Radiotherapy for a repeatedly recurrent ameloblastoma with malignant transformation. Head Neck. 2014;36:E1–3. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed. 23257. - PubMed
-
- Eversole LR, Leider AS, Strub D. Radiographic characteristics of cystogenic ameloblastoma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1984;57:572–7. - PubMed
-
- Carlson ER, Marx RE. The ameloblastoma:Primary curative surgical management. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2006;64:484–94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joms. 2005.11.032. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
