Comparison of Surface Topography Changes from Conventional Metal Brackets and Self-Ligating Metal Brackets after Immersion in Three Different Mouthwashes using Atomic Force Microscopy: An in vitro Study
- PMID: 37654337
- PMCID: PMC10466524
- DOI: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_78_23
Comparison of Surface Topography Changes from Conventional Metal Brackets and Self-Ligating Metal Brackets after Immersion in Three Different Mouthwashes using Atomic Force Microscopy: An in vitro Study
Abstract
In orthodontics, the surface roughness and corrosion behavior due to metal ion releases in orthodontic brackets and archwires affect the effectiveness of tooth movement. Atomic force microscopy (AFM) can provide three-dimensional information measurements which are used to evaluate the quantitative analysis of the surface changes of orthodontic brackets. Stainless steel orthodontic brackets and wires can release metal ions which lead to corrosion when exposed to various types of mouthwash.
Aim: The main aim of this study is to compare and evaluate the surface changes from conventional metal brackets and self-ligating metal brackets after immersion in three different mouthwashes.
Materials and methods: Sixteen conventional metal brackets and sixteen metal self-ligating brackets were evenly grouped and immersed in deionized water, chlorhexidine mouthwash, herbal mouthwash, and betadine mouthwash for seven days and the surface changes were evaluated using nondestructive AFM.
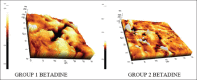
Results: The surface roughness was evaluated at 30 μm and the results showed that more surface roughness was observed P < 0.05 in betadine mouthwash groups and followed by herbal mouthwash and least in chlorhexidine mouthwash.
Conclusion: Based on the AFM results, the surface changes were more pronounced in both groups which were immersed in betadine and herbal mouthwash than others and the choice of mouthwash should be considered before prescribing to the patients.
Keywords: Atomic force microscopy; conventional orthodontic brackets; self-ligating brackets; surface changes.
Copyright: © 2023 Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Huang HH. Variation in surface topography of different NiTi orthodontic archwires in various commercial fluoride-containing environments. Dent Mater. 2007;23:24–33. - PubMed
-
- Huang H-H, Chiu Y-H, Lee T-H, Wu S-C, Yang H-W, Su K-H, et al. Ion release from NiTi orthodontic wires in artificial saliva with various acidities. Biomaterials. 2003;24:3585–92. - PubMed
-
- Kao CT, Huang TH. Variations in surface characteristics and corrosion behaviour of metal brackets and wires in different electrolyte solutions. Eur J Orthod. 2010;32:555–60. - PubMed
-
- Choi S, Joo HJ, Cheong Y, Park YG, Park HK. Effects of self-ligating brackets on the surfaces of stainless steel wires following clinical use:AFM investigation. J Microsc. 2012;246:53–9. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous