Cardiac dysfunction in severe pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: the right ventricle in search of the right therapy
- PMID: 37654664
- PMCID: PMC10466806
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1216538
Cardiac dysfunction in severe pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: the right ventricle in search of the right therapy
Abstract
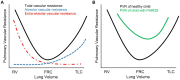
Severe acute respiratory distress syndrome in children, or PARDS, carries a high risk of morbidity and mortality that is not fully explained by PARDS severity alone. Right ventricular (RV) dysfunction can be an insidious and often under-recognized complication of severe PARDS that may contribute to its untoward outcomes. Indeed, recent evidence suggest significantly worse outcomes in children who develop RV failure in their course of PARDS. However, in this narrative review, we highlight the dearth of evidence regarding the incidence of and risk factors for PARDS-associated RV dysfunction. While we wish to draw attention to the absence of available evidence that would inform recommendations around surveillance and treatment of RV dysfunction during severe PARDS, we leverage available evidence to glean insights into potentially helpful surveillance strategies and therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: children; echocardiography (Echo); extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO); pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome (PARDS); right ventricular (RV) dysfunction.
Copyright © 2023 Webb, Burton, Manchikalapati, Prabhakaran, Loberger and Richter.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Yehya N, Smith L, Thomas NJ, Steffen KM, Zimmerman J, Lee JH, et al. Definition, incidence, and epidemiology of pediatric acute respiratory distress syndrome: from the second Pediatric Acute Lung Injury Consensus Conference. Pediatr Crit Care Med. (2023) 24:S87–98. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000003161 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

