Prevalence of PIK3CA mutations in Taiwanese patients with breast cancer: a retrospective next-generation sequencing database analysis
- PMID: 37655108
- PMCID: PMC10466395
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1192946
Prevalence of PIK3CA mutations in Taiwanese patients with breast cancer: a retrospective next-generation sequencing database analysis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer is the most common cancer type that affects women. In hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced breast cancer (ABC), phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate 3-kinase catalytic subunit alpha (PIK3CA) is the most frequently mutated gene associated with poor prognosis. This study evaluated the frequency of PIK3CA mutations in the Taiwanese breast cancer population.
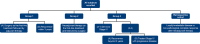
Methodology: This is a retrospective study; patient data were collected for 2 years from a next-generation sequencing database linked to electronic health records (EHRs). The primary endpoint was the regional prevalence of PIK3CA mutation. The secondary endpoints were to decipher the mutation types across breast cancer subtype, menopausal status, and time to treatment failure after everolimus (an mTOR inhibitor) or cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 (CDK4/6) inhibitor treatment.
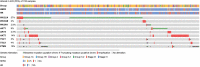
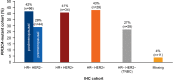
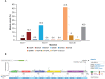
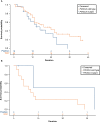
Results: PIK3CA mutations were identified in 278 of 728 patients (38%). PIK3CA mutations were reported in 43% of patients with HR-/HER2+ subtype and 42% of patients with HR+/HER2- postmenopausal status. A lower prevalence of PIK3CA mutations was observed in triple-negative (27%) and HR+/HER2- premenopausal patients (29%). The most common mutation was at exon 20 (H1047R mutation, 41.6%), followed by exon 9 (E545K mutation, 18.9% and E542K mutation, 10.3%). Among patients treated with CDK4/6 inhibitors, the median time to treatment failure was 12 months (95% CI: 7-21 months) in the PIK3CA mutation cohort and 16 months (95% CI: 11-23 months) in the PIK3CA wild-type cohort, whereas patients receiving an mTOR inhibitor reported a median time to treatment failure of 20.5 months (95% CI: 8-33 months) in the PIK3CA mutation cohort and 6 months (95% CI: 2-9 months) in the PIK3CA wild-type cohort.
Conclusion: A high frequency of PIK3CA mutations was detected in Taiwanese patients with breast cancer, which was consistent with previous studies. Early detection of PIK3CA mutations might influence therapeutic decisions, leading to better treatment outcomes.
Keywords: PIK3CA mutations; Taiwanese population; advanced breast cancer; hotspot mutations; next-generation sequencing.
Copyright © 2023 Chao, Tsai, Liu, Lien, Lin, Feng, Chen, Lai, Hsu, Lynn, Huang and Tseng.
Conflict of interest statement
Author JL is full time employee of Novartis. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The authors declare his study was supported by Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. The funder was involved in the study design and medical writing assistance was provided by Caamin Arora, M Pharm, from Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation, India.
Figures

Similar articles
-
PIK3CA gene mutation status associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer: a retrospective cohort study.BMC Cancer. 2025 Feb 27;25(1):365. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-13486-5. BMC Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40016671 Free PMC article.
-
[PIK3CA gene mutations in Chinese women with HR+/HER2- breast cancer].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Dec 8;51(12):1246-1250. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20220506-00371. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36480834 Chinese.
-
[Characteristic PIK3CA gene mutation in breast cancer].Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2025 Mar 8;54(3):243-249. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112151-20240817-00543. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2025. PMID: 40032415 Chinese.
-
PIK3CA mutation status, progression and survival in advanced HR + /HER2- breast cancer: a meta-analysis of published clinical trials.BMC Cancer. 2022 Sep 21;22(1):1002. doi: 10.1186/s12885-022-10078-5. BMC Cancer. 2022. PMID: 36131248 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus versus alpelisib in advanced hormone receptor-positive HER2-negative breast cancer: targeting different nodes of the PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway with different clinical implications.Breast Cancer Res. 2020 Apr 6;22(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s13058-020-01271-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32252811 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between PIK3R1 Expression and Cell Growth in Human Breast Cancer Cell Line BT-474 and Clinical Outcomes.World J Oncol. 2025 Feb;16(1):131-141. doi: 10.14740/wjon1986. Epub 2025 Jan 10. World J Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39850525 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Alterations of Tumors in HER2-Low Breast Cancers.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 21;25(2):1318. doi: 10.3390/ijms25021318. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38279318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- André F, Ciruelos EM, Juric D, Loibl S, Campone M, Mayer IA, et al. . Alpelisib plus fulvestrant for PIK3CA-mutated, hormone receptor-positive, human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-negative advanced breast cancer: final overall survival results from SOLAR-1. Ann Oncol (2021) 32(2):208–17. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.11.011 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

