Particle radiotherapy for breast cancer
- PMID: 37655110
- PMCID: PMC10467264
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1107703
Particle radiotherapy for breast cancer
Abstract
Breast cancer is the most common malignant tumor in female patients. Along with surgery, radiotherapy is one of the most commonly prescribed treatments for breast cancer. Over the past few decades, breast cancer radiotherapy technology has significantly improved. Nevertheless, related posttherapy complications should not be overlooked. Common complications include dose-related coronary toxicity, radiation pneumonia, and the risk of second primary cancer of the contralateral breast. Particle radiotherapy with protons or carbon ions is widely attracting interest as a potential competitor to conventional photon radiotherapy because of its superior physical and biological characteristics. This article summarizes the results of clinical research on proton and carbon-ion radiotherapy for treating breast cancer.
Keywords: breast cancer; carbon ion; particle; photon; proton; radiotherapy.
Copyright © 2023 Ruan, Okamoto, Ohno, Li and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
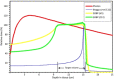
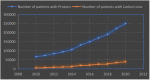


References
-
- Overgaard M, Nielsen HM, Tramm T, Højris I, Grantzau TL, Alsner J, et al. . Postmastectomy radiotherapy in high-risk breast cancer patients given adjuvant systemic therapy. A 30-year long-term report from the danish breast cancer cooperative group DBCG 82bc trial. Radiother Oncol (2022) 170:4–13. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2022.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Meattini I, Becherini C, Boersma L, Kaidar-Person O, Marta GN, Montero A, et al. . European Society for Radiotherapy and Oncology Advisory Committee in Radiation Oncology Practice consensus recommendations on patient selection and dose and fractionation for external beam radiotherapy in early breast cancer. Lancet Oncol (2022) 23(1):e21–31. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00539-8 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

