H3K27 acetylation-induced FSTL1 upregulation by P300/RUNX1 co-activation exacerbated autophagy-mediated neuronal damage and NF-κB-stimulated inflammation in Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 37655275
- PMCID: PMC10465437
- DOI: 10.1007/s10616-023-00589-9
H3K27 acetylation-induced FSTL1 upregulation by P300/RUNX1 co-activation exacerbated autophagy-mediated neuronal damage and NF-κB-stimulated inflammation in Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
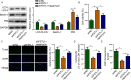
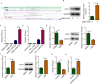
Follistatin-like protein 1 (FSTL1) has been demonstrated to participate in the pathogenesis of several neurological diseases. The current study informed the role of H3K27 acetylation-induced FSTL1 upregulation in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Our investigation discovered the upregulated FSTL1 expression and enhanced autophagy activity in AD. FSTL1 knockdown successfully attenuated the injuries of Aβ1-42-challenged SH-SY5Y cells through the inhibition of autophagy activity. Besides, FSTL1 deficiency suppresses the inflammatory response and NF-κB signaling in AD. Moreover, it was found that p300 was recruited by transcriptional factor RUNX1 to stimulate the H3K27 acetylation in FSTL1 promoter region, which caused the upregulation of FSTL1 in AD. To summarize, p300 acted as a co-activator of RUNX1 to trigger the activation of FSTL1 in AD, resulting in the exacerbated injuries and inflammatory responses of Aβ1-42-induced SH-SY5Y cells.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Autophagy; FSTL1; H3K27 acetylation; Inflammation.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature B.V. 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



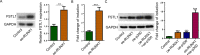
Similar articles
-
FSTL1-knockdown improves neural oscillation via decreasing neuronal-inflammation regulating apoptosis in Aβ1-42 induced AD model mice.Exp Neurol. 2023 Jan;359:114231. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2022.114231. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Exp Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36162512
-
Inhibition of long non-coding RNA HOXA11-AS against neuroinflammation in Parkinson's disease model via targeting miR-124-3p mediated FSTL1/NF-κB axis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Apr 4;13(8):11455-11469. doi: 10.18632/aging.202837. Epub 2021 Apr 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33839699 Free PMC article.
-
Follistatin-like 1 promotes osteoclast formation via RANKL-mediated NF-κB activation and M-CSF-induced precursor proliferation.Cell Signal. 2016 Sep;28(9):1137-1144. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2016.05.018. Epub 2016 May 24. Cell Signal. 2016. PMID: 27234130
-
Follistatin-like protein 1 and its role in inflammation and inflammatory diseases.Immunol Res. 2014 Aug;59(1-3):266-72. doi: 10.1007/s12026-014-8526-z. Immunol Res. 2014. PMID: 24838142 Review.
-
FSTL1: A double-edged sword in cancer development.Gene. 2024 May 15;906:148263. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2024.148263. Epub 2024 Feb 10. Gene. 2024. PMID: 38346455 Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

