Dissecting the novel abilities of aripiprazole: The generation of anti-colorectal cancer effects by targeting G α q via HTR2B
- PMID: 37655314
- PMCID: PMC10465950
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.015
Dissecting the novel abilities of aripiprazole: The generation of anti-colorectal cancer effects by targeting G α q via HTR2B
Abstract
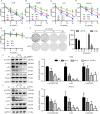
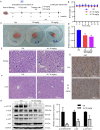
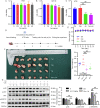
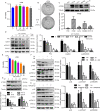
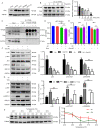
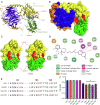
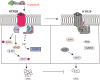
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a type of malignant tumor that seriously threatens human health and life, and its treatment has always been a difficulty and hotspot in research. Herein, this study for the first time reports that antipsychotic aripiprazole (Ari) against the proliferation of CRC cells both in vitro and in vivo, but with less damage in normal colon cells. Mechanistically, the results showed that 5-hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor (HTR2B) and its coupling protein G protein subunit alpha q (Gαq) were highly distributed in CRC cells. Ari had a strong affinity with HTR2B and inhibited HTR2B downstream signaling. Blockade of HTR2B signaling suppressed the growth of CRC cells, but HTR2B was not found to have independent anticancer activity. Interestingly, the binding of Gαq to HTR2B was decreased after Ari treatment. Knockdown of Gαq not only restricted CRC cell growth, but also directly affected the anti-CRC efficacy of Ari. Moreover, an interaction between Ari and Gαq was found in that the mutation at amino acid 190 of Gαq reduced the efficacy of Ari. Thus, these results confirm that Gαq coupled to HTR2B was a potential target of Ari in mediating CRC proliferation. Collectively, this study provides a novel effective strategy for CRC therapy and favorable evidence for promoting Ari as an anticancer agent.
Keywords: 5-Hydroxytryptamine 2B receptor; 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor; Aripiprazole; Colorectal cancer; Extracellular regulated protein kinases; G protein subunit alpha q; Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/the serine threonine kinase AKT.
© 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased Serotonin Signaling Contributes to the Warburg Effect in Pancreatic Tumor Cells Under Metabolic Stress and Promotes Growth of Pancreatic Tumors in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2017 Jul;153(1):277-291.e19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 28315323
-
Activated G alpha q inhibits p110 alpha phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt.J Biol Chem. 2003 Jun 27;278(26):23472-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M212232200. Epub 2003 Apr 18. J Biol Chem. 2003. PMID: 12704201
-
Low Doses of the Anti-psychotic Drug Aripiprazole Have Strong P-gp-inhibitory Activity and Sensitize Anti-mitotic Drug-resistant Cancer Cells.Anticancer Res. 2018 Sep;38(9):5101-5108. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.12830. Anticancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30194155
-
Gαq signalling: the new and the old.Cell Signal. 2014 May;26(5):833-48. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.01.010. Epub 2014 Jan 17. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24440667 Review.
-
Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Potential of the G Protein, Gα/q,11.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015 Mar 24;2:14. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2015.00014. eCollection 2015. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015. PMID: 26664886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol (CBD) and Colorectal Tumorigenesis: Potential Dual Modulatory Roles via the Serotonergic Pathway.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jun 26;32(7):375. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32070375. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40710186 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonin signalling in cancer: Emerging mechanisms and therapeutic opportunities.Clin Transl Med. 2024 Jul;14(7):e1750. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.1750. Clin Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38943041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting HTR2B suppresses nonfunctioning pituitary adenoma growth and sensitizes cabergoline treatment via inhibiting Gαq/PLC/PKCγ/STAT3 axis.Neuro Oncol. 2024 Nov 4;26(11):2010-2026. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/noae130. Neuro Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38989697 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfation of chondroitin and bile acids converges to antagonize Wnt/β-catenin signaling and inhibit APC deficiency-induced gut tumorigenesis.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024 Mar;14(3):1241-1256. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.12.006. Epub 2023 Dec 16. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2024. PMID: 38487006 Free PMC article.
-
The Antipsychotic Drug Aripiprazole Suppresses Colorectal Cancer by Targeting LAMP2a to Induce RNH1/miR-99a/mTOR-Mediated Autophagy and Apoptosis.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Dec;11(48):e2409498. doi: 10.1002/advs.202409498. Epub 2024 Nov 8. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 39513392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Fuchs H.E., Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. - PubMed
-
- Grothey A., Fakih M., Tabernero J. Management of BRAF-mutant metastatic colorectal cancer: a review of treatment options and evidence-based guidelines. Ann Oncol. 2021;32:959–967. - PubMed
-
- Keum N., Giovannucci E. Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;16:713–732. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

