The neuroprotective effect of traditional Chinese medicinal plants-A critical review
- PMID: 37655317
- PMCID: PMC10465969
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.06.009
The neuroprotective effect of traditional Chinese medicinal plants-A critical review
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Author correction to "The neuroprotective effect of traditional Chinese medicinal plants-A critical review" [Acta Pharm Sin B 13 (2023) 3208-3237].Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025 Apr;15(4):2300. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2024.12.002. Epub 2024 Dec 3. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2025. PMID: 40486845 Free PMC article.
Abstract
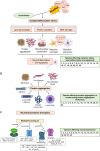
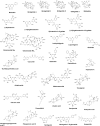
Neurodegenerative and neuropsychiatric diseases are increasingly affecting individuals' quality of life, thus increasing their cost to social and health systems. These diseases have overlapping mechanisms, such as oxidative stress, protein aggregation, neuroinflammation, neurotransmission impairment, mitochondrial dysfunction, and excitotoxicity. Currently, there is no cure for neurodegenerative diseases, and the available therapies have adverse effects and low efficacy. For neuropsychiatric disorders, such as depression, the current therapies are not adequate to one-third of the patients, the so-called treatment-resistant patients. So, searching for new treatments is fundamental. Medicinal plants appear as a strong alternative and complement towards new treatment protocols, as they have been used for health purposes for thousands of years. Thus, the main goal of this review is to revisit the neuroprotective potential of some of the most predominant medicinal plants (and one fungus) used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), focusing on their proven mechanisms of action and their chemical compositions, to give clues on how they can be useful against neurodegeneration progression.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Clinical trials; Depression; Medicinal plants; Neurodegeneration; Oxidative stress; Parkinson's disease; Toxicology.
© 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Figures


References
-
- Allkin B. In: State of the world's plants 2017. Willis K., editor. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew; London (UK): 2017. Useful plants–medicines: at least 28,187 plant species are currently recorded as being of medicinal use; pp. 22–29. - PubMed
-
- Polaris Market Research Market research report. https://www.polarismarketresearch.com/industry-analysis/herbal-medicine-... Available from:
-
- Duthey B. Background paper 6.11 Alzheimer disease and other dementias, update on 2004. 2013. http://www.who.int/medicines/areas/priority_medicines/BP6_11Alzheimer.pdf Available from:
-
- OCED . 2017. Health at a glance 2017, Paris.https://www.oecd-ilibrary.org/social-issues-migration-health/health-at-a... Available from:
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

