Rapidly separating dissolving microneedles with sustained-release colchicine and stabilized uricase for simplified long-term gout management
- PMID: 37655319
- PMCID: PMC10466003
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.011
Rapidly separating dissolving microneedles with sustained-release colchicine and stabilized uricase for simplified long-term gout management
Abstract
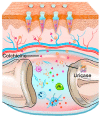
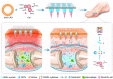
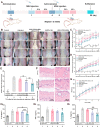
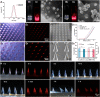
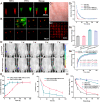
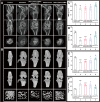
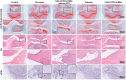
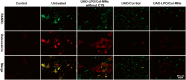
Despite growing prevalence and incidence, the management of gout remains suboptimal. The intermittent nature of the gout makes the long-term urate-lowering therapy (ULT) particularly important for gout management. However, patients are reluctant to take medication day after day to manage incurable occasional gout flares, and suffer from possible long-term toxicity. Therefore, a safe and easy-to-operate drug delivery system with simple preparation for the long-term management of gout is very necessary. Here, a chitosan-containing sustained-release microneedle system co-loaded with colchicine and uricase liposomes were fabricated to achieve this goal. This microneedle system was confirmed to successfully deliver the drug to the skin and maintain a one-week drug retention. Furthermore, its powerful therapeutic potency to manage gout was investigated in both acute gouty and chronic gouty models. Besides, the drug co-delivery system could help avoid long-term daily oral colchicine, a drug with a narrow therapeutic index. This system also avoids mass injection of uricase by improving its stability, enhancing the clinical application value of uricase. In general, this two-drug system reduces the dosage of uricase and colchicine and improves the patient's compliance, which has a strong clinical translation.
Keywords: Colchicine; Gout management; Liposome; Long-term urate-lowering therapy; Microneedles; Sustained-release; Transdermal administration; Uricase.
© 2023 Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences. Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Transdermal delivery of colchicine using dissolvable microneedle arrays for the treatment of acute gout in a rat model.Drug Deliv. 2022 Dec;29(1):2984-2994. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2022.2122632. Drug Deliv. 2022. PMID: 36101018 Free PMC article.
-
The challenges of gout management in the elderly.Drugs Aging. 2011 Aug 1;28(8):591-603. doi: 10.2165/11592750-000000000-00000. Drugs Aging. 2011. PMID: 21812496 Review.
-
Management of acute and chronic gouty arthritis: present state-of-the-art.Drugs. 2004;64(21):2399-416. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200464210-00003. Drugs. 2004. PMID: 15481999 Review.
-
Zhengqing fengtongning sustained-release tablets prevents gout flares in the process of ULT: A randomized, positive control, double-blind, double-simulation, multicenter trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 May 6;101(18):e29199. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000029199. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35550468 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Therapeutic approaches in the treatment of gout.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020 Jun;50(3S):S24-S30. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2020.04.010. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2020. PMID: 32620199 Review.
Cited by
-
Development and Evaluation of Huperzine A-Loaded Microneedles for Transdermal Delivery and Pretreatment of GD Poisoning.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025 Jun 6;26(5):164. doi: 10.1208/s12249-025-03149-w. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2025. PMID: 40481368
-
A Bibliometric Analysis of Microneedle-Mediated Drug Delivery: Trends, Hotspots, and Future Directions.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025 May 10;19:3805-3825. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S519048. eCollection 2025. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2025. PMID: 40376038 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progressive microneedles for targeting and intelligent drug delivery.Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025 Jun;20(3):101051. doi: 10.1016/j.ajps.2025.101051. Epub 2025 Mar 28. Asian J Pharm Sci. 2025. PMID: 40503059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cutting-edge microneedle innovations: Transforming the landscape of cardiovascular and metabolic disease management.iScience. 2024 Jul 31;27(9):110615. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110615. eCollection 2024 Sep 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39224520 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advances in materials science for ocular diseases induced by cardiovascular risk factors.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025 Jun 27;13:1618232. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2025.1618232. eCollection 2025. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2025. PMID: 40657159 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gout Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2019;5:68. - PubMed
-
- Dalbeth N., Gosling A.L., Gaffo A., Abhishek A. Gout. Lancet. 2021;397:1843–1855. - PubMed
-
- Dehlin M., Jacobsson L., Roddy E. Global epidemiology of gout: prevalence, incidence, treatment patterns and risk factors. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16:380–390. - PubMed
-
- FitzGerald J.D., Dalbeth N., Mikuls T., Brignardello-Petersen R., Guyatt G., Abeles A.M., et al. 2020 American college of rheumatology guideline for the management of gout. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020;72:879–895. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

