Efficacy of clove and tulsi supplementation in drinking water in broiler immunity
- PMID: 37655435
- PMCID: PMC10650245
- DOI: 10.1002/vms3.1250
Efficacy of clove and tulsi supplementation in drinking water in broiler immunity
Abstract
Background: Medicinal plants or their products are popular substitutes for antibiotics or other synthetic growth promoters for their beneficial effects and cost-effectiveness. Clove (Cv) and tulsi (Ts) are rich in phytochemicals and are used to augment the growth performance of poultry.
Objectives: The current investigation was carried out to evaluate the effects of Cv and Ts supplementation in drinking water on the morphologic and morphometric adaptations in the lymphoid organs.
Methods: The experiment was conducted on 60 broiler chicks, divided into 4 homogenous groups (5 pens/group and 3 broilers/pen) named T0 (control), T1 (0.5% Cv and 2% Ts), T2 (1% Cv and 3% Ts) and T3 (1.5% Cv and 4% Ts). The treatments were administered from days 8 to 28. Lymphoid organs (thymus, spleen and bursa of Fabricius) were collected on days 14, 21 and 28 after sacrificing five broilers from each group.
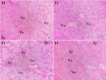
Results: The treatment groups had higher thymus and spleen weights on day 21, whereas the weights of the bursa of Fabricius were higher on days 14, 21 and 28. In the histomorphologic study, no noticeable difference in the histoarchitectures of the lymphoid organs was noticed. However, substantial differences in the cortico-medullary ratio and the number of follicles in the thymus and bursa of Fabricius, respectively, were found in the histomorphometric investigation.
Conclusion: The inclusion of Cv and Ts in drinking water augments the weight of lymphoid organs with histomorphometric adaptations that might improve the immune status in broilers.
Keywords: bursa of Fabricius; medicinal plants; phytochemicals; spleen; thymus.
© 2023 The Authors. Veterinary Medicine and Science published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have a conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Modulation of growth performance, gut morphometry, and cecal microbiota in broilers by clove (Syzygium aromaticum) and tulsi (Ocimum sanctum) supplementation.Poult Sci. 2023 Jan;102(1):102266. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.102266. Epub 2022 Oct 20. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 36370662 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of clove buds powder supplementation on hematological profile, biochemical parameters, lymphoid organs, and cell-mediated immunity of broilers.Open Vet J. 2023 Jul;13(7):854-863. doi: 10.5455/OVJ.2023.v13.i7.7. Epub 2023 Jul 31. Open Vet J. 2023. PMID: 37614736 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of dietary dexamethasone on the morphologic and morphometric adaptations in the lymphoid organs and mortality rate in broilers.Vet Med Sci. 2023 Jul;9(4):1656-1665. doi: 10.1002/vms3.1139. Epub 2023 Apr 17. Vet Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 37067539 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Clove and Tulsi on broiler health and meat production.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023 Jun;30(6):103654. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2023.103654. Epub 2023 Apr 15. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37152300 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of ginger extract and/or propolis extract on immune system parameters of vaccinated broilers.Poult Sci. 2023 Oct;102(10):102903. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102903. Epub 2023 Jul 6. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37506621 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akter, S. , Khan, M. Z. , Jahan, M. R. , Karim, M. R. , & Islam, M. R. (2006). Histomorphological study of the lymphoid tissues of broiler chickens. Bangladesh Journal of Veterinary Medicine, 4(2), 87–92. 10.3329/bjvm.v4i2.1289 - DOI
-
- Batiha, G. E. , Alkazmi, L. M. , Wasef, L. G. , Beshbishy, A. M. , Nadwa, E. H. , & Rashwan, E. K. (2020). Syzygium aromaticum L. (Myrtaceae): Traditional uses, bioactive chemical constituents, pharmacological and toxicological activities. Biomolecules, 10(2), 202. 10.3390/biom10020202 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chowdhury, S. , Mandal, G. P. , Patra, A. K. , Kumar, P. , Samanta, I. , Pradhan, S. , & Samanta, A. K. (2018). Different essential oils in diets of broiler chickens: 2. Gut microbes and morphology, immune response, and some blood profile and antioxidant enzymes. Animal Feed Science and Technology, 236, 39–47. 10.1016/j.anifeedsci.2017.12.003 - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

