Divergent roles of Rad4 and Rad23 homologs in Metarhizium robertsii's resistance to solar ultraviolet damage
- PMID: 37655890
- PMCID: PMC10537586
- DOI: 10.1128/aem.00994-23
Divergent roles of Rad4 and Rad23 homologs in Metarhizium robertsii's resistance to solar ultraviolet damage
Abstract
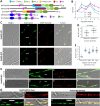
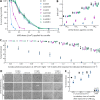
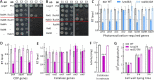
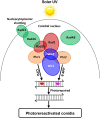
The anti-ultraviolet (UV) role of a Rad4-Rad23-Rad33 complex in budding yeast relies on nucleotide excision repair (NER), which is mechanistically distinct from photorepair of DNA lesions generated under solar UV irradiation but remains poorly known in filamentous fungi. Here, two nucleus-specific Rad4 paralogs (Rad4A and Rad4B) and nucleocytoplasmic shuttling Rad23 ortholog are functionally characterized by multiple analyses of their null mutants in Metarhizium robertsii, an entomopathogenic fungus lacking Rad33. Rad4A was proven to interact with Rad23 and contribute significantly more to conidial UVB resistance (90%) than Rad23 (65%). Despite no other biological function, Rad4A exhibited a very high activity in photoreactivation of UVB-impaired/inactivated conidia by 5-h light exposure due to its interaction with Rad10, an anti-UV protein clarified previously to have acquired a similar photoreactivation activity through its interaction with a photolyase in M. robertsii. The NER activity of Rad4A or Rad23 was revealed by lower reactivation rates of moderately impaired conidia after 24-h dark incubation but hardly observable at the end of 12-h dark incubation, suggesting an infeasibility of its NER activity in the field where nighttime is too short. Aside from a remarkable contribution to conidial UVB resistance, Rad23 had pleiotropic effect in radial growth, aerial conidiation, antioxidant response, and cell wall integrity but no photoreactivation activity. However, Rad4B proved redundant in function. The high photoreactivation activity of Rad4A unveils its essentiality for M. robertsii's fitness to solar UV irradiation and is distinct from the yeast homolog's anti-UV role depending on NER. IMPORTANCE Resilience of solar ultraviolet (UV)-impaired cells is crucial for the application of fungal insecticides based on formulated conidia. Anti-UV roles of Rad4, Rad23, and Rad33 rely upon nucleotide excision repair (NER) of DNA lesions in budding yeast. Among two Rad4 paralogs and Rad23 ortholog characterized in Metarhizium robertsii lacking Rad33, Rad4A contributes to conidial UVB resistance more than Rad23, which interacts with Rad4A rather than functionally redundant Rad4B. Rad4A acquires a high activity in photoreactivation of conidia severely impaired or inactivated by UVB irradiation through its interaction with Rad10, another anti-UV protein previously proven to interact with a photorepair-required photolyase. The NER activity of either Rad4A or Rad23 is seemingly extant but unfeasible under field conditions. Rad23 has pleiotropic effect in the asexual cycle in vitro but no photoreactivation activity. Therefore, the strong anti-UV role of Rad4A depends on photoreactivation, unveiling a scenario distinct from the yeast homolog's NER-reliant anti-UV role.
Keywords: anti-UV proteins; fungal insecticidal cells; photoreactivation; solar irradiation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative Roles of Rad4A and Rad4B in Photoprotection of Beauveria bassiana from Solar Ultraviolet Damage.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jan 23;9(2):154. doi: 10.3390/jof9020154. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36836269 Free PMC article.
-
Photoprotective Role of Photolyase-Interacting RAD23 and Its Pleiotropic Effect on the Insect-Pathogenic Fungus Beauveria bassiana.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020 May 19;86(11):e00287-20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00287-20. Print 2020 May 19. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32245759 Free PMC article.
-
Rad2, Rad14 and Rad26 recover Metarhizium robertsii from solar UV damage through photoreactivation in vivo.Microbiol Res. 2024 Mar;280:127589. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127589. Epub 2023 Dec 23. Microbiol Res. 2024. PMID: 38154444
-
Recovery of insect-pathogenic fungi from solar UV damage: Molecular mechanisms and prospects.Adv Appl Microbiol. 2024;129:59-82. doi: 10.1016/bs.aambs.2024.04.003. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39389708 Review.
-
Molecular basis and regulatory mechanisms underlying fungal insecticides' resistance to solar ultraviolet irradiation.Pest Manag Sci. 2022 Jan;78(1):30-42. doi: 10.1002/ps.6600. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Pest Manag Sci. 2022. PMID: 34397162 Review.
Cited by
-
Photoreactivation Activities of Rad5, Rad16A and Rad16B Help Beauveria bassiana to Recover from Solar Ultraviolet Damage.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Jun 13;10(6):420. doi: 10.3390/jof10060420. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38921406 Free PMC article.
-
The Forkhead Box Gene, MaSep1, Negatively Regulates UV- and Thermo-Tolerances and Is Required for Microcycle Conidiation in Metarhizium acridum.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Aug 2;10(8):544. doi: 10.3390/jof10080544. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39194870 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

