The Influence of Selected Insecticides on the Oxidative Response of Atta sexdens (Myrmicinae, Attini) Workers
- PMID: 37656416
- PMCID: PMC10695876
- DOI: 10.1007/s13744-023-01077-7
The Influence of Selected Insecticides on the Oxidative Response of Atta sexdens (Myrmicinae, Attini) Workers
Abstract
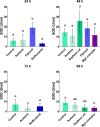
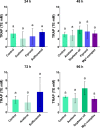
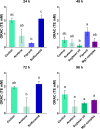
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated as products of normal cellular metabolic activities; however, the use of pesticides to control leafcutter ants leads to unbalanced ROS production. We evaluated the effects of two insecticides (fipronil, sulfluramid) and metallic insecticide complex (magnesium complex [Mg(hesp)2(phen)] (1)) on the superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH) and the overall antioxidant capacity using two different methodologies: total radical-trapping potential (TRAP) and oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC). Media workers of Atta sexdens (C. Linnaeus) were exposed to the insecticides for 24 h, 48 h, 72 h and 96 h before their fat bodies were dissected for analysis. The results showed that although the sulfluramid may cause the production of ROS, its slow action in the organism does not lead to oxidative stress. There is a rise in oxidative stress in workers of leafcutter ants treated with fipronil because SOD significantly increased when compared to the control group. On the other hand, Mg1-complex suppressed both GSH and SOD, indicating that the immune system may be affected by Mg1-complex, which has a delayed activity ideal for its use in chemical pest control. Both TRAP and ORAC evaluated total antioxidant capacities; however, ORAC proved to be a more sensitive method. In conclusion, the Mg1-complex is a new compound that should be further investigated as a potential replacement for fipronil and sulfluramid in pest control.
Keywords: Antioxidant; Fipronil; Flavonoid; Magnesium complex; Sulfluramid.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Contamination routes and mortality of the leaf-cutting ant Atta sexdens (Hymenoptera: Formicidae) by the insecticides fipronil and sulfluramid through social interactions.Pest Manag Sci. 2021 Oct;77(10):4411-4417. doi: 10.1002/ps.6475. Epub 2021 May 26. Pest Manag Sci. 2021. PMID: 33982404
-
Allogrooming, Self-grooming, and Touching Behavior as a Mechanism to Disperse Insecticides Inside Colonies of a Leaf-Cutting Ant.Neotrop Entomol. 2022 Feb;51(1):73-80. doi: 10.1007/s13744-021-00927-6. Epub 2021 Nov 17. Neotrop Entomol. 2022. PMID: 34787836
-
Transmission Electron Microscopy as a Tool to Study the Toxicological Effects of Thiamethoxam in Workers of Atta sexdens (Myrmicinae, Attini).Microsc Microanal. 2021 Feb;27(1):170-186. doi: 10.1017/S1431927620024733. Microsc Microanal. 2021. PMID: 33280633
-
Comparison of in vitro tests for antioxidant and immunomodulatory capacities of compounds.Phytomedicine. 2014 Jan 15;21(2):164-71. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.08.008. Epub 2013 Sep 14. Phytomedicine. 2014. PMID: 24041614 Review.
-
The effects of dietary restriction on oxidative stress in rodents.Free Radic Biol Med. 2014 Jan;66:88-99. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.037. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Free Radic Biol Med. 2014. PMID: 23743291 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Insects as Sentinels of Oxidative Stress Induced by Environmental Contaminants: Biomarkers and Analytical Approaches.Toxics. 2025 Aug 20;13(8):698. doi: 10.3390/toxics13080698. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40863974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baker BP, Grant JA, Malakar-Kuenen R (2018) Soybean oil profile, NYS IPM Type: Minimum Risk Pesticide, New York State IPM Program. https://hdl.handle.net/1813/56142
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

