Pharmacokinetics of Orbital Topotecan After Ophthalmic Artery Chemosurgery and Intravenous Infusion in the Swine Model
- PMID: 37656475
- PMCID: PMC10479255
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.64.12.3
Pharmacokinetics of Orbital Topotecan After Ophthalmic Artery Chemosurgery and Intravenous Infusion in the Swine Model
Abstract
Purpose: Surgery, multiagent systemic chemotherapy, and radiation are used for patients with orbital retinoblastoma but are associated with unacceptable short- and long-term toxicity (including death). We studied orbital and systemic exposure of topotecan in the swine model after ophthalmic artery chemosurgery (OAC) and intravenous (IV) delivery.
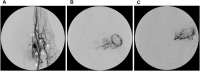
Methods: Landrace pigs (n = 3) underwent 30-minute OAC of topotecan (4 mg), and samples were serially obtained from the femoral artery and from a microdialysis probe inserted into the lateral rectus muscle sheath of the infused eye as a surrogate of the orbital irrigation. Animals were recovered, and, after a wash-out period, plasma and microdialysate samples from the contralateral eye were collected after a 30-minute IV infusion of topotecan (4 mg). Samples were quantified by high-performance liquid chromatography, and population pharmacokinetic analysis was conducted using MonolixSuite.
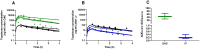
Results: After OAC, median topotecan exposure in the orbit was 5624 ng × h/mL (range 3922-12531) compared to 23 ng × h/mL (range 18-75) after IV infusion. Thus, topotecan exposure in the orbit was 218-fold (range 75-540) higher after OAC than after IV infusion despite comparable systemic exposure (AUCpl) between routes (AUCpl, OAC: 141 ng × h/mL [127-191] versus AUCpl, IV: 139 ng × h/mL [126-186]). OAC was more selective to target the orbit because the median (range) orbital-to-plasma exposure ratio was 44 (28-65) after OAC compared to 0.18 (0.13-0.40) after IV infusion.
Conclusions: OAC of topotecan resulted in higher orbital exposure than after IV infusion and was a more selective route for local drug delivery. Patients with orbital retinoblastoma may benefit from a multimodal treatment strategy including OAC therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure:
Figures
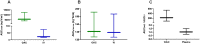
References
-
- Chantada G, Fandiño A, Casak S, Manzitti J, Raslawski E, Schvartzman E.. Treatment of overt extraocular retinoblastoma. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003; 40: 158–161. - PubMed
-
- Chantada GL, Guitter MR, Fandiño AC, et al. .. Treatment results in patients with retinoblastoma and invasion to the cut end of the optic nerve. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009; 52: 218–222. - PubMed
-
- Chawla B, Hasan F, Seth R, et al. .. Multimodal therapy for Stage III retinoblastoma (international retinoblastoma staging system): a prospective comparative study. Ophthalmology. 2016; 123(9): 1933–1939. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

