Irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence is mediated by constitutive MYC degradation
- PMID: 37656618
- PMCID: PMC10591853
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113079
Irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence is mediated by constitutive MYC degradation
Abstract
Cells can irreversibly exit the cell cycle and become senescent to safeguard against uncontrolled proliferation. While the p53-p21 and p16-Rb pathways are thought to mediate senescence, they also mediate reversible cell cycle arrest (quiescence), raising the question of whether senescence is actually reversible or whether alternative mechanisms underly the irreversibility associated with senescence. Here, we show that senescence is irreversible and that commitment to and maintenance of senescence are mediated by irreversible MYC degradation. Senescent cells start dividing when a non-degradable MYC mutant is expressed, and quiescent cells convert to senescence when MYC is knocked down. In early oral carcinogenesis, epithelial cells exhibit MYC loss and become senescent as a safeguard against malignant transformation. Later stages of oral premalignant lesions exhibit elevated MYC levels and cellular dysplasia. Thus, irreversible cell cycle exit associated with senescence is mediated by constitutive MYC degradation, but bypassing this degradation may allow tumor cells to escape during cancer initiation.
Keywords: CDK4/6; CP: Cell biology; MEK; MYC; cell cycle; palbociclib; pre-malignant lesions; senescence; time-lapse imaging; trametinib.
Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
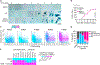

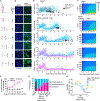
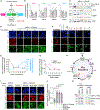
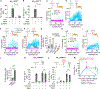

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

