Unravelling the gut-lung axis: insights into microbiome interactions and Traditional Indian Medicine's perspective on optimal health
- PMID: 37656879
- PMCID: PMC10508358
- DOI: 10.1093/femsec/fiad103
Unravelling the gut-lung axis: insights into microbiome interactions and Traditional Indian Medicine's perspective on optimal health
Abstract
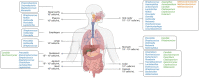
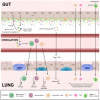
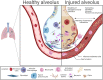
The microbiome of the human gut is a complex assemblage of microorganisms that are in a symbiotic relationship with one another and profoundly influence every aspect of human health. According to converging evidence, the human gut is a nodal point for the physiological performance matrixes of the vital organs on several axes (i.e. gut-brain, gut-lung, etc). As a result of COVID-19, the importance of gut-lung dysbiosis (balance or imbalance) has been realised. In view of this, it is of utmost importance to develop a comprehensive understanding of the microbiome, as well as its dysbiosis. In this review, we provide an overview of the gut-lung axial microbiome and its importance in maintaining optimal health. Human populations have successfully adapted to geophysical conditions through traditional dietary practices from around the world. In this context, a section has been devoted to the traditional Indian system of medicine and its theories and practices regarding the maintenance of optimally customized gut health.
Keywords: COVID-19; Gut-lung axis; dysbiosis; microbiome; traditional medicine.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abreu MT. Toll-like receptor signalling in the intestinal epithelium: how bacterial recognition shapes intestinal function. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:131–44. - PubMed
-
- Agnivesha . 15th chapter. Chikitsa Shtana, Charaka Samhita. Y. T. Acharya. Varanasi: Chaukhambha Sanskrit Samsthan; 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

