Overlapping representations of food and social stimuli in mouse VTA dopamine neurons
- PMID: 37657441
- PMCID: PMC11672631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.003
Overlapping representations of food and social stimuli in mouse VTA dopamine neurons
Abstract
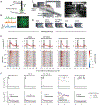
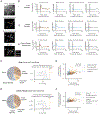
Dopamine neurons of the ventral tegmental area (VTADA) respond to food and social stimuli and contribute to both forms of motivation. However, it is unclear whether the same or different VTADA neurons encode these different stimuli. To address this question, we performed two-photon calcium imaging in mice presented with food and conspecifics and found statistically significant overlap in the populations responsive to both stimuli. Both hunger and opposite-sex social experience further increased the proportion of neurons that respond to both stimuli, implying that increasing motivation for one stimulus increases overlap. In addition, single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed significant co-expression of feeding- and social-hormone-related genes in individual VTADA neurons. Taken together, our functional and transcriptional data suggest overlapping VTADA populations underlie food and social motivation.
Keywords: dopamine; hunger; internal state; motivation; snRNA-seq; social; two-photon calcium imaging; ventral tegmental area.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Update of
-
Overlapping representations of food and social stimuli in VTA dopamine neurons.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 May 17:2023.05.17.541104. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.17.541104. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Neuron. 2023 Nov 15;111(22):3541-3553.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2023.08.003. PMID: 37293057 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

