A Multipathway Phosphopeptide Standard for Rapid Phosphoproteomics Assay Development
- PMID: 37657519
- PMCID: PMC10561125
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100639
A Multipathway Phosphopeptide Standard for Rapid Phosphoproteomics Assay Development
Abstract
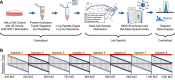
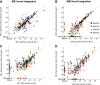
Recent advances in methodology have made phosphopeptide analysis a tractable problem for many proteomics researchers. There are now a wide variety of robust and accessible enrichment strategies to generate phosphoproteomes while free or inexpensive software tools for quantitation and site localization have simplified phosphoproteome analysis workflow tremendously. As a research group under the Association for Biomolecular Resource Facilities umbrella, the Proteomics Standards Research Group has worked to develop a multipathway phosphopeptide standard based on a mixture of heavy-labeled phosphopeptides designed to enable researchers to rapidly develop assays. This mixture contains 131 mass spectrometry vetted phosphopeptides specifically chosen to cover as many known biologically interesting phosphosites as possible from seven different signaling networks: AMPK signaling, death and apoptosis signaling, ErbB signaling, insulin/insulin-like growth factor-1 signaling, mTOR signaling, PI3K/AKT signaling, and stress (p38/SAPK/JNK) signaling. Here, we describe a characterization of this mixture spiked into a HeLa tryptic digest stimulated with both epidermal growth factor and insulin-like growth factor-1 to activate the MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathways. We further demonstrate a comparison of phosphoproteomic profiling of HeLa performed independently in five labs using this phosphopeptide mixture with data-independent acquisition. Despite different experimental and instrumentation processes, we found that labs could produce reproducible, harmonized datasets by reporting measurements as ratios to the standard, while intensity measurements showed lower consistency between labs even after normalization. Our results suggest that widely available, biologically relevant phosphopeptide standards can act as a quantitative "yardstick" across laboratories and sample preparations enabling experimental designs larger than a single laboratory can perform. Raw data files are publicly available in the MassIVE dataset MSV000090564.
Keywords: data-independent acquisition; mass spectrometry; phosphopeptide; phosphorylation; proteomics; stable isotope label; targeted.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest B. C. S. is a founder and shareholder in Proteome Software, which operates in the field of proteomics. A. J. N. and J. M. R. are employees of Cell Signaling Technology. A. W. H. and B. P. are employees of Thermo Fisher Scientific.
Figures

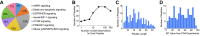




Similar articles
-
Targeted phosphoproteomics of insulin signaling using data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry.Sci Signal. 2015 Jun 9;8(380):rs6. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.aaa3139. Sci Signal. 2015. PMID: 26060331
-
Quantitative Proteome and Phosphoproteome Profiling in Magnaporthe oryzae.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2356:109-119. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1613-0_9. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34236681
-
SPECHT - single-stage phosphopeptide enrichment and stable-isotope chemical tagging: quantitative phosphoproteomics of insulin action in muscle.J Proteomics. 2015 Jan 30;114:48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 9. J Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25463755 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies for mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics using isobaric tagging.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021 Sep;18(9):795-807. doi: 10.1080/14789450.2021.1994390. Epub 2021 Oct 28. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2021. PMID: 34652972 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomic analysis of phosphorylation in cancer.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014 Jun;11(3):259-67. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2014.901156. Epub 2014 Mar 26. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2014. PMID: 24666026 Review.
Cited by
-
Quality Control in the Mass Spectrometry Proteomics Core: A Practical Primer.J Biomol Tech. 2024 Sep 12;35(3):3fc1f5fe.42308a9a. doi: 10.7171/3fc1f5fe.42308a9a. eCollection 2024 Sep 30. J Biomol Tech. 2024. PMID: 40331211 Free PMC article.
-
A framework for quality control in quantitative proteomics.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Aug 11:2024.04.12.589318. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.12.589318. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Proteome Res. 2024 Oct 4;23(10):4392-4408. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00363. PMID: 38645098 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Computational approaches to identify sites of phosphorylation.Proteomics. 2024 Apr;24(8):e2300088. doi: 10.1002/pmic.202300088. Epub 2023 Dec 24. Proteomics. 2024. PMID: 37897210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Framework for Quality Control in Quantitative Proteomics.J Proteome Res. 2024 Oct 4;23(10):4392-4408. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.4c00363. Epub 2024 Sep 9. J Proteome Res. 2024. PMID: 39248652 Free PMC article.
-
Spike-in enhanced phosphoproteomics uncovers synergistic signaling responses to MEK inhibition in colon cancer cells.Nat Commun. 2025 May 27;16(1):4884. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-59404-y. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40419504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen P. Protein kinases—the major drug targets of the twenty-first century? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2002;1:309–315. - PubMed
-
- Ferguson F.M., Gray N.S. Kinase inhibitors: the road ahead. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018;17:353–377. - PubMed
-
- Andersson L., Porath J. Isolation of phosphoproteins by immobilized metal (Fe3+) affinity chromatography. Anal. Biochem. 1986;154:250–254. - PubMed
-
- Stensballe A., Andersen S., Jensen O.N. Characterization of phosphoproteins from electrophoretic gels by nanoscale Fe(III) affinity chromatography with off-line mass spectrometry analysis. Proteomics. 2001;1:207–222. - PubMed
-
- Pinkse M.W.H., Uitto P.M., Hilhorst M.J., Ooms B., Heck A.J.R. Selective isolation at the femtomole level of phosphopeptides from proteolytic digests using 2D-NanoLC-ESI-MS/MS and titanium oxide precolumns. Anal. Chem. 2004;76:3935–3943. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

