UPS writes a new saga of SAGA
- PMID: 37657588
- PMCID: PMC10843445
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2023.194981
UPS writes a new saga of SAGA
Abstract
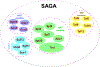
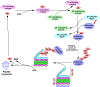
SAGA (Spt-Ada-Gcn5-Acetyltransferase), an evolutionarily conserved transcriptional co-activator among eukaryotes, is a large multi-subunit protein complex with two distinct enzymatic activities, namely HAT (Histone acetyltransferase) and DUB (De-ubiquitinase), and is targeted to the promoter by the gene-specific activator proteins for histone covalent modifications and PIC (Pre-initiation complex) formation in enhancing transcription (or gene activation). Targeting of SAGA to the gene promoter is further facilitated by the 19S RP (Regulatory particle) of the 26S proteasome (that is involved in targeted degradation of protein via ubiquitylation) in a proteolysis-independent manner. Moreover, SAGA is also recently found to be regulated by the 26S proteasome in a proteolysis-dependent manner via the ubiquitylation of its Sgf73/ataxin-7 component that is required for SAGA's integrity and DUB activity (and hence transcription), and is linked to various diseases including neurodegenerative disorders and cancer. Thus, SAGA itself and its targeting to the active gene are regulated by the UPS (Ubiquitin-proteasome system) with implications in diseases.
Keywords: SAGA; Sgf73 and ataxin-7; Transcription; UPS.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
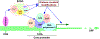

Similar articles
-
Sus1p facilitates pre-initiation complex formation at the SAGA-regulated genes independently of histone H2B de-ubiquitylation.J Mol Biol. 2014 Aug 12;426(16):2928-2941. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2014.05.028. Epub 2014 Jun 6. J Mol Biol. 2014. PMID: 24911582 Free PMC article.
-
A novel ubiquitin-proteasome system regulation of Sgf73/ataxin-7 that maintains the integrity of the coactivator SAGA in orchestrating transcription.Genetics. 2023 Jul 6;224(3):iyad071. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad071. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37075097 Free PMC article.
-
Two Distinct Regulatory Mechanisms of Transcriptional Initiation in Response to Nutrient Signaling.Genetics. 2018 Jan;208(1):191-205. doi: 10.1534/genetics.117.300518. Epub 2017 Nov 15. Genetics. 2018. PMID: 29141908 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation by SAGA and TFIID.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Feb;1809(2):97-108. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2010.08.009. Epub 2010 Aug 26. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 20800707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SAGA unveiled.Trends Biochem Sci. 2005 Jan;30(1):7-10. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2004.11.007. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005. PMID: 15653319 Review.
Cited by
-
The Peptide PROTAC Modality: A New Strategy for Drug Discovery.MedComm (2020). 2025 Mar 24;6(4):e70133. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70133. eCollection 2025 Apr. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40135198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unraveling role of ubiquitination in drug resistance of gynecological cancer.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 May 15;14(5):2523-2537. doi: 10.62347/WYKZ9784. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38859858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Roeder RG (2005) Transcriptional regulation and the role of diverse coactivators in animal cells. FEBS Lett., 579: 909–15. - PubMed
-
- Bhaumik SR, and Malik S (2008) Diverse regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic transcriptional activation by the proteasome complex. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol., 43: 419–33. - PubMed
-
- Durairaj G, Malik S, and Bhaumik SR (2017) Regulatory mechanisms of eukaryotic gene expression. Gene regulation, Epigenetics and Hormone Signaling (Editor: Mandal S). Wiley-VCH, Germany. Volume 1: 1–28.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

