Decrease of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder
- PMID: 37657958
- PMCID: PMC10964357
- DOI: 10.1016/j.abd.2023.01.003
Decrease of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder
Abstract
Background: Primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-Cell lymphoproliferative disorder (PC-SMTLD) has been considered as a controversial dermatological disease that has been included in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma group, presenting most commonly as a solitary nodule and/or plaque with a specific and characteristic head and neck predilection. Due to the considerable overlap between PC-SMTLD and pseudolymphoma (PL), the differential diagnosis is often challenging. Methylation of DNA at position 5 of cytosine, and the subsequent reduction in intracellular 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) levels, is a key epigenetic event in several cancers, including systemic lymphomas. However, it has rarely been studied in cutaneous lymphomas.
Objectives: The authors aimed to explore the role of differential 5-hmC immunostaining as a useful marker to distinguish PC-SMTLD from PL.
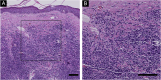
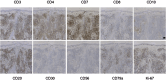
Methods: Retrospective case series study with immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence analysis of 5-hmC was performed in PL and PC-SMTLD.
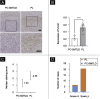
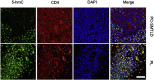
Results: Significant decrease of 5-hmC nuclear staining was observed in PC-SMTLD when compared with PL (p < 0.0001). By semi-quantitative grade integration, there were statistical differences in the final 5-hmC scores in the two study groups. The IF co-staining of 5-hmC with CD4 revealed a decrease of 5-hmC in CD4+ lymphocytes of PC-SMTLD.
Study limitations: The small clinical sample size of the study.
Conclusions: The immunorreactivity of 5-hmC in CD4+ lymphocytes was highly suggestive of a benign process as PL. Furthermore, the decrease of 5-hmC nuclear staining in PC-SMTLD indicated its lymphoproliferative status and helped to make the differential diagnosis with PL.
Keywords: Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; DNA methylation; Epigenomics.
Copyright © 2023 Sociedade Brasileira de Dermatologia. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Differential NFATc1 Expression in Primary Cutaneous CD4+ Small/Medium-Sized Pleomorphic T-Cell Lymphoma and Other Forms of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma and Pseudolymphoma.Am J Dermatopathol. 2017 Feb;39(2):95-103. doi: 10.1097/DAD.0000000000000597. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017. PMID: 27097342
-
The Clinical Spectrum of Primary Cutaneous CD4+ Small/Medium-Sized Pleomorphic T-Cell Lymphoproliferative Disorder: An Updated Systematic Literature Review and Case Series.Dermatology. 2021;237(4):618-628. doi: 10.1159/000511473. Epub 2020 Dec 16. Dermatology. 2021. PMID: 33326960
-
Loss of expression of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in CD30-positive cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders.J Cutan Pathol. 2014 Dec;41(12):901-6. doi: 10.1111/cup.12411. Epub 2014 Nov 25. J Cutan Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25353265
-
CD30+ T cell enriched primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium sized pleomorphic T cell lymphoma: A distinct variant of indolent CD4+ T cell lymphoproliferative disease.Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017 Oct;30:52-58. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2017.04.009. Epub 2017 Apr 27. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017. PMID: 28965629
-
Primary cutaneous small- to medium-sized CD4+ pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma: a retrospective case series and review of the provisional cutaneous lymphoma category.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011 Dec 1;12(6):389-401. doi: 10.2165/11590390-000000000-00000. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2011. PMID: 21863906 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances in classification and treatment of primary cutaneous lymphomas.Ann Hematol. 2025 Apr;104(4):2143-2157. doi: 10.1007/s00277-025-06311-3. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Ann Hematol. 2025. PMID: 40131416 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cetinözman F., Jansen P.M., Willemze R. Expression of programmed death-1 in primary cutaneous CD4-positive small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma, cutaneous pseudo-T-cell lymphoma, and other types of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Keeling B.H., Gavino A.C.P., Admirand J., Soldano A.C. Primary cutaneous CD4-positive small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoproliferative disorder: report of a case and review of the literature. J Cutan Pathol. 2017;44:944–947. - PubMed
-
- Magro C.M., Momtahen S. Differential NFATc1 expression in primary cutaneous CD4+ small/medium-sized pleomorphic T-cell lymphoma and other forms of cutaneous T-Cell lymphoma and pseudolymphoma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:95–103. - PubMed
-
- Sundram U. Cutaneous lymphoproliferative disorders: what’s new in the revised 4th edition of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Adv Anat Pathol. 2019;26:93–113. - PubMed
-
- Nakagawa Y., Hamada T., Takahashi T., Miyake T., Hirai Y., Iwatsuki K., et al. Analysis of clonality in cutaneous B-cell lymphoma and B-cell pseudolymphoma using skin flow cytometry: Comparison of immunophenotyping and gene rearrangement studies. J Dermatol. 2022;49:246–252. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

