Interferon signaling restrains renal cell carcinoma heterogeneity
- PMID: 37658022
- PMCID: PMC11075004
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trecan.2023.08.008
Interferon signaling restrains renal cell carcinoma heterogeneity
Abstract
Type I interferon (IFN) is central to cancer surveillance as it mediates both direct and immune-mediated oncosuppressive effects. A recent study by Perelli et al. suggests that the ability of renal cancer cells to tolerate complex karyotypic alterations elicited by chromosomal instability (CIN), and ultimately acquire full metastatic potential, is also negatively regulated by IFN signaling.
Keywords: CGAS; CNV; cancer stem cells; cancer/immunity coevolution; immunoevasion.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests P.H. and J.F. are full-time employees of Sotio a.s. L.G. is/has been holding research contracts with Lytix Biopharma, Promontory, and Onxeo, has received consulting/advisory honoraria from Boehringer Ingelheim, AstraZeneca, OmniSEQ, Onxeo, The Longevity Labs, Inzen, Imvax, Sotio, Promontory, Noxopharm, EduCom, and the Luke Heller TECPR2 Foundation, and holds Promontory stock options.
Figures
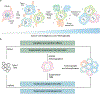
Comment on
-
Interferon signaling promotes tolerance to chromosomal instability during metastatic evolution in renal cancer.Nat Cancer. 2023 Jul;4(7):984-1000. doi: 10.1038/s43018-023-00584-1. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Nat Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37365326 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

