Ranking Research Methodology by Risk - a cross-sectional study to determine the opinion of research ethics committee members
- PMID: 37658420
- PMCID: PMC10472668
- DOI: 10.1186/s13643-023-02295-1
Ranking Research Methodology by Risk - a cross-sectional study to determine the opinion of research ethics committee members
Abstract
Background: When reviewing a protocol, research ethics committees (RECs, equivalent to institutional review boards - IRBs) have the responsibility to consider whether the proposed research is justified. If research is not justified, it can waste participants' time, researchers' time and resources. As RECs are not constituted to cover all areas of scientific or academic expertise, it can be difficult for RECs to decide whether research is scientifically or methodologically justified especially in the absence of authoritative (often in the form of systematic) reviews. Where such reviews are absent, some have argued that RECs should insist on a new review of existing evidence as a condition of the REC favourable opinion. However, as RECs review a wide range of research, such requests must be proportionate to the type, and extent, of proposed projects. Risk is one factor that may influence the extent of evidence need for a REC to determine that the new project is justified, but not the only factor. The aim of the work described here was to determine whether REC members and researchers specifically link risk to the type of research methodology, and if so, whether this link could be used to help guide the need for systematic, or other, types of reviews.
Method: We conducted a cross-sectional study, gathering data between November 2020 and January 2021, to examine whether proposed research methodologies impact how RECs perceive risk to participants. We presented 31 research methodologies to REC members and researchers in the form of an international survey.
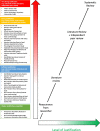
Results: We collected 283 responses that included both qualitative and quantitative data as to how research methodology impacts perceptions of risk to participants. We used the data to conclude that RECs did see a link between risk and type of research. We therefore constructed a hierarchy of risk with Phase 1 and 2 clinical trials, and clinical psychology/psychiatry intervention studies, at the top (i.e. viewed as most risky).
Conclusions: We discuss whether this hierarchy is useful for guiding RECs as to the level of scientific justification that they should seek when reviewing proposed research protocols, and present a one-page guidance sheet to help RECs during their reviews.
Keywords: Ethics committees; Harm; IRB; Institutional review boards; REC; Research methodology; Risk; Systematic reviews.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors received conference and travel funding from the EVBRES project. SEK is a trustee of the UK Research Integrity Office (UKRIO) and chairs research ethics committees for the UK’s Ministry of Defence, Health Security Agency ,and Health Research Authority.
Figures
References
-
- Cooper JA, McNair L. Scientific review by the ethics committee. Jo Empirical Res Hum Res Ethics. 2014: 9. - PubMed
-
- Lund H, Brunnhuber K, Juhl C, Robinson K, Leenaars M, Dorch BF, et al. Towards evidence based research. BMJ (Online). 2016;355. - PubMed
-
- Health Research Authority. Peer / scientific review of research and the role of NRES Research Ethics Committees (RECs). 2012 Cited 2023 Mar 14. Available from: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/documents/60/peer-scientific-review-of-research-a....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials