MicroMagnify: A Multiplexed Expansion Microscopy Method for Pathogens and Infected Tissues
- PMID: 37658522
- PMCID: PMC10602566
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202302249
MicroMagnify: A Multiplexed Expansion Microscopy Method for Pathogens and Infected Tissues
Abstract
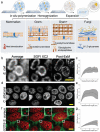
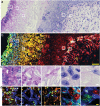
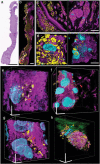
Super-resolution optical imaging tools are crucial in microbiology to understand the complex structures and behavior of microorganisms such as bacteria, fungi, and viruses. However, the capabilities of these tools, particularly when it comes to imaging pathogens and infected tissues, remain limited. MicroMagnify (µMagnify) is developed, a nanoscale multiplexed imaging method for pathogens and infected tissues that are derived from an expansion microscopy technique with a universal biomolecular anchor. The combination of heat denaturation and enzyme cocktails essential is found for robust cell wall digestion and expansion of microbial cells and infected tissues without distortion. µMagnify efficiently retains biomolecules suitable for high-plex fluorescence imaging with nanoscale precision. It demonstrates up to eightfold expansion with µMagnify on a broad range of pathogen-containing specimens, including bacterial and fungal biofilms, infected culture cells, fungus-infected mouse tone, and formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded human cornea infected by various pathogens. Additionally, an associated virtual reality tool is developed to facilitate the visualization and navigation of complex 3D images generated by this method in an immersive environment allowing collaborative exploration among researchers worldwide. µMagnify is a valuable imaging platform for studying how microbes interact with their host systems and enables the development of new diagnosis strategies against infectious diseases.
Keywords: expansion microscopy; infected tissue; microbiology; multiplexing.
© 2023 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Y.Z., A.K., and F.F. are inventors on several inventions related to ExM methods.
Figures



Update of
-
MicroMagnify: a multiplexed expansion microscopy method for pathogens and infected tissues.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 6:rs.3.rs-2637060. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2637060/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(30):e2302249. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302249. PMID: 36945526 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
Similar articles
-
MicroMagnify: a multiplexed expansion microscopy method for pathogens and infected tissues.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2023 Mar 6:rs.3.rs-2637060. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2637060/v1. Res Sq. 2023. Update in: Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Oct;10(30):e2302249. doi: 10.1002/advs.202302249. PMID: 36945526 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Universal Molecular Retention with 11-Fold Expansion Microscopy.J Vis Exp. 2023 Oct 6;(200). doi: 10.3791/65338. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 37870360
-
Super-Resolution Vibrational Imaging Using Expansion Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022 Jul;9(20):e2200315. doi: 10.1002/advs.202200315. Epub 2022 May 6. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022. PMID: 35521971 Free PMC article.
-
Expansion microscopy: enabling single cell analysis in intact biological systems.FEBS J. 2019 Apr;286(8):1482-1494. doi: 10.1111/febs.14597. Epub 2018 Jul 9. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 29938896 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peritonsillar abscess: clinical aspects of microbiology, risk factors, and the association with parapharyngeal abscess.Dan Med J. 2017 Mar;64(3):B5333. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28260599 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzymatically enhanced ultrastructure expansion microscopy unlocks expansion of in vitro Toxoplasma gondii cysts.mSphere. 2024 Sep 25;9(9):e0032224. doi: 10.1128/msphere.00322-24. Epub 2024 Aug 27. mSphere. 2024. PMID: 39189782 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrastructure expansion microscopy (U-ExM) of mouse and human kidneys for analysis of subcellular structures.Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024 Nov;81(11):618-638. doi: 10.1002/cm.21870. Epub 2024 May 7. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 2024. PMID: 38715433
-
Accelerated protein retention expansion microscopy using microwave radiation.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 12:2024.05.11.593228. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.11.593228. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Dec 16;4(12):100907. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100907. PMID: 38766072 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Highly accurate image registration for 3D multiplexed cyclic imaging using dense labeling in expandable tissue gels.PLoS Biol. 2025 Jul 3;23(7):e3003240. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3003240. eCollection 2025 Jul. PLoS Biol. 2025. PMID: 40608767 Free PMC article.
-
Accelerated protein retention expansion microscopy using microwave radiation.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Dec 16;4(12):100907. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100907. Epub 2024 Nov 22. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 39579759 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
