Autophagy-mediated surveillance of Rim4-mRNA interaction safeguards programmed meiotic translation
- PMID: 37659076
- PMCID: PMC10591816
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113051
Autophagy-mediated surveillance of Rim4-mRNA interaction safeguards programmed meiotic translation
Abstract
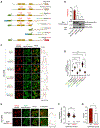
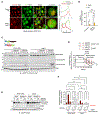
In yeast meiosis, autophagy is active and essential. Here, we investigate the fate of Rim4, a meiosis-specific RNA-binding protein (RBP), and its associated transcripts during meiotic autophagy. We demonstrate that Rim4 employs a nuclear localization signal (NLS) to enter the nucleus, where it loads its mRNA substrates before nuclear export. Upon reaching the cytoplasm, active autophagy selectively spares the Rim4-mRNA complex. During meiotic divisions, autophagy preferentially degrades Rim4 in an Atg11-dependent manner, coinciding with the release of Rim4-bound mRNAs for translation. Intriguingly, these released mRNAs also become vulnerable to autophagy. In vitro, purified Rim4 and its RRM-motif-containing variants activate Atg1 kinase in meiotic cell lysates and in immunoprecipitated (IP) Atg1 complexes. This suggests that the conserved RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) of Rim4 are involved in stimulating Atg1 and thereby facilitating selective autophagy. Taken together, our findings indicate that autophagy surveils Rim4-mRNA interaction to ensure stage-specific translation during meiosis.
Keywords: Atg1; Atg11; CP: Cell biology; Pab1; RBP; Rim4; mRNAs; meiosis; nucleus; selective autophagy.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Regulation of Rim4 distribution, function, and stability during meiosis by PKA, Cdc14, and 14-3-3 proteins.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113052. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113052. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37659077 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Rim4 distribution, function, and stability during meiosis by PKA, Cdc14, and 14-3-3 proteins.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113052. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113052. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37659077 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-mediated post-transcriptional surveillance of meiotic translation in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae.Autophagy. 2024 Mar;20(3):694-696. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2276632. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37927068 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy prevents runaway meiotic divisions.Autophagy. 2020 May;16(5):969-970. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2020.1739449. Epub 2020 Mar 15. Autophagy. 2020. PMID: 32150508 Free PMC article.
-
Vir1p, the yeast homolog of virilizer, is required for mRNA m6A methylation and meiosis.Genetics. 2023 May 4;224(1):iyad043. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad043. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 36930734 Free PMC article.
-
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae poly (A) binding protein (Pab1): Master regulator of mRNA metabolism and cell physiology.Yeast. 2019 Jan;36(1):23-34. doi: 10.1002/yea.3347. Epub 2018 Oct 17. Yeast. 2019. PMID: 30006991 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulation of Rim4 distribution, function, and stability during meiosis by PKA, Cdc14, and 14-3-3 proteins.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113052. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113052. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37659077 Free PMC article.
-
Rim4-seeded stress granules connect temperature sensing to meiotic regulation.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5566. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60645-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593583 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic Cytokinesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Spores That Just Need Closure.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;10(2):132. doi: 10.3390/jof10020132. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Autophagy-mediated post-transcriptional surveillance of meiotic translation in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae.Autophagy. 2024 Mar;20(3):694-696. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2276632. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37927068 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

