Regulation of Rim4 distribution, function, and stability during meiosis by PKA, Cdc14, and 14-3-3 proteins
- PMID: 37659077
- PMCID: PMC10591911
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113052
Regulation of Rim4 distribution, function, and stability during meiosis by PKA, Cdc14, and 14-3-3 proteins
Abstract
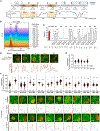
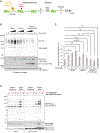
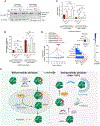
Meiotic gene expression in budding yeast is tightly controlled by RNA-binding proteins (RBPs), with the meiosis-specific RBP Rim4 playing a key role in sequestering mid-late meiotic transcripts to prevent premature translation. However, the mechanisms governing assembly and disassembly of the Rim4-mRNA complex, critical for Rim4's function and stability, remain poorly understood. In this study, we unveil regulation of the Rim4 ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complex by the yeast 14-3-3 proteins Bmh1 and Bmh2. These proteins form a Rim4-Bmh1-Bmh2 heterotrimeric complex that expels mRNAs from Rim4 binding. We identify four Bmh1/2 binding sites (BBSs) on Rim4, with two residing within the RNA recognition motifs (RRMs). Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of serine/threonine (S/T) residues at these BBSs by PKA kinase and Cdc14 phosphatase activities primarily control formation of Rim4-Bmh1/2, regulating Rim4's subcellular distribution, function, and stability. These findings shed light on the intricate post-transcriptional regulatory mechanisms governing meiotic gene expression.
Keywords: 14-3-3 proteins; CP: Cell biology; Cdc14; PKA; Rim4; autophagy; de-phosphorylation; kinase; meiosis; phosphatase; phosphorylation.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment on
-
Autophagy-mediated surveillance of Rim4-mRNA interaction safeguards programmed meiotic translation.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113051. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113051. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37659076 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Autophagy-mediated post-transcriptional surveillance of meiotic translation in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae.Autophagy. 2024 Mar;20(3):694-696. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2276632. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37927068 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-mediated surveillance of Rim4-mRNA interaction safeguards programmed meiotic translation.Cell Rep. 2023 Sep 26;42(9):113051. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113051. Epub 2023 Sep 1. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 37659076 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of 14-3-3 proteins, Polo kinase, and RNA-binding protein Pes4 as key regulators of meiotic commitment in budding yeast.Curr Biol. 2022 Apr 11;32(7):1534-1547.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.022. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Curr Biol. 2022. PMID: 35240051 Free PMC article.
-
The Multiple Roles of the Cdc14 Phosphatase in Cell Cycle Control.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jan 21;21(3):709. doi: 10.3390/ijms21030709. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31973188 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-transcriptional regulation in budding yeast meiosis.Curr Genet. 2016 May;62(2):313-5. doi: 10.1007/s00294-015-0546-2. Epub 2015 Nov 27. Curr Genet. 2016. PMID: 26613728 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The yeast 14-3-3 proteins Bmh1 and Bmh2 regulate key signaling pathways.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jan 24;11:1327014. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1327014. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38328397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meiotic Cytokinesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Spores That Just Need Closure.J Fungi (Basel). 2024 Feb 6;10(2):132. doi: 10.3390/jof10020132. J Fungi (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38392804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assembly and function of the amyloid-like translational repressor Rim4 is coupled with nutrient conditions.EMBO J. 2023 Dec 1;42(23):e113332. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022113332. Epub 2023 Nov 3. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37921330 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy-mediated post-transcriptional surveillance of meiotic translation in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae.Autophagy. 2024 Mar;20(3):694-696. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2023.2276632. Epub 2023 Nov 5. Autophagy. 2024. PMID: 37927068 Free PMC article.
-
Rim4-seeded stress granules connect temperature sensing to meiotic regulation.Nat Commun. 2025 Jul 1;16(1):5566. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60645-0. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40593583 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

