Protocol of a parallel, randomized controlled trial on the effects of a novel personalized nutrition approach by artificial intelligence in real world scenario
- PMID: 37660022
- PMCID: PMC10474697
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-16434-9
Protocol of a parallel, randomized controlled trial on the effects of a novel personalized nutrition approach by artificial intelligence in real world scenario
Abstract
Background: Nutrition service needs are huge in China. Previous studies indicated that personalized nutrition (PN) interventions were effective. The aim of the present study is to identify the effectiveness and feasibility of a novel PN approach supported by artificial intelligence (AI).
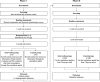
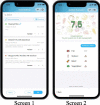
Methods: This study is a two-arm parallel, randomized, controlled trial in real world scenario. The participants will be enrolled among who consume lunch at a staff canteen. In Phase I, a total of 170 eligible participants will be assigned to either intervention or control group on 1:1 ratio. The intervention group will be instructed to use the smartphone applet to record their lunches and reach the real-time AI-based information of dish nutrition evaluation and PN evaluation after meal consumption for 3 months. The control group will receive no nutrition information but be asked to record their lunches though the applet. Dietary pattern, body weight or blood pressure optimizing is expected after the intervention. In phase II, the applet will be free to all the diners (about 800) at the study canteen for another one year. Who use the applet at least 2 days per week will be regarded as the intervention group while the others will be the control group. Body metabolism normalization is expected after this period. Generalized linear mixed models will be used to identify the dietary, anthropometric and metabolic changes.
Discussion: This novel approach will provide real-time AI-based dish nutrition evaluation and PN evaluation after meal consumption in order to assist users with nutrition information to make wise food choice. This study is designed under a real-life scenario which facilitates translating the trial intervention into real-world practice.
Trial registration: This trial has been registered with the Chinese Clinical Trial Registry (ChiCTR2100051771; date registered: 03/10/2021).
Keywords: Artificial intelligence; Nutrition intervention; Personalized nutrition; Real world; Smartphone applet.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

