hsa_circ_0003596, as a novel oncogene, regulates the malignant behavior of renal cell carcinoma by modulating glycolysis
- PMID: 37660068
- PMCID: PMC10474667
- DOI: 10.1186/s40001-023-01288-z
hsa_circ_0003596, as a novel oncogene, regulates the malignant behavior of renal cell carcinoma by modulating glycolysis
Abstract
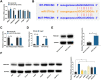
Background: This research was planned to analyze hsa_circ_0003596 (circCOL5A1) and glycolysis-focused mechanisms in renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
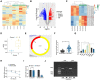
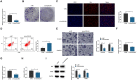
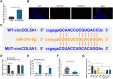
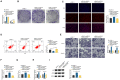
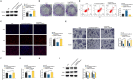
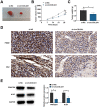
Methods: circCOL5A1, miR-370-5p, and PRKCSH levels were determined in RCC tissues and selected cell lines by RT-qPCR and/or Western blot. RCC cells after corresponding transfection were tested by colony formation assay, EdU assay, Transwell assay, and flow cytometry to analyze cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and apoptosis. Meanwhile, glycolysis in cells was evaluated by measuring glucose consumption, lactic acid, and ATP production, as well as immunoblotting for HK2 and PKM2. In addition, circCOL5A1 knockdown was performed in animal experiments to observe tumor growth and glycolysis. Finally, the ceRNA network between circCOL5A1, miR-370-5p, and PRKCSH was studied by luciferase reporter assay and RIP experiment.
Results: circCOL5A1 and PRKCSH were highly expressed and miR-370-5p was poorly expressed in RCC. circCOL5A1 knockdown depressed RCC proliferation, invasion, migration, and glycolysis, and enhanced apoptosis. circCOL5A1 competitively adsorbed miR-370-5p. Artificial upregulation of miR-370-5p saved the pro-tumor effect of circCOL5A1 on RCC cells, as evidenced by suppression of tumor malignancy and glycolysis. miR-370-5p targeted PRKCSH. PRKCSH overexpression contributed to a reversal of the anti-tumor effect of circCOL5A1 silencing. Silencing circCOL5A1 inhibited RCC tumor growth and glycolysis.
Conclusions: circCOL5A1 regulates the malignant behavior of RCC by modulating glycolysis.
Keywords: Glycolysis; Renal cell carcinoma; hsa_circ_0003596; miR-370-5p; PRKCSH.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circ_0000069 contributes to the growth, metastasis and glutamine metabolism in renal cell carcinoma (RCC) via regulating miR-125a-5p-dependent SLC1A5 expression.Transpl Immunol. 2023 Apr;77:101764. doi: 10.1016/j.trim.2022.101764. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Transpl Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36462557
-
Circ_0005875 sponges miR-502-5p to promote renal cell carcinoma progression through upregulating E26 transformation specific-1.Anticancer Drugs. 2022 Jan 1;33(1):e286-e298. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001205. Anticancer Drugs. 2022. PMID: 34407050
-
CircCOL5A1 inhibits proliferation, migration, invasion, and extracellular matrix production of keloid fibroblasts by regulating the miR-877-5p/EGR1 axis.Burns. 2023 Feb;49(1):137-148. doi: 10.1016/j.burns.2021.12.013. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Burns. 2023. PMID: 35184918
-
Silencing circular RNA circ_0054537 and upregulating microRNA-640 suppress malignant progression of renal cell carcinoma via regulating neuronal pentraxin-2 (NPTX2).Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):8279-8295. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1984002. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34565284 Free PMC article.
-
CircRNA SCARB1 Promotes Renal Cell Carcinoma Progression Via Mir- 510-5p/SDC3 Axis.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020;20(6):461-470. doi: 10.2174/1568009620666200409130032. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2020. PMID: 32271695
Cited by
-
Multiple roles of circular RNAs in prostate cancer: from the biological basis to potential clinical applications.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Feb 27;30(1):140. doi: 10.1186/s40001-025-02382-0. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 40016786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the impact of circRNAs on cancer glycolysis: Insights into tumor progression and therapeutic strategies.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 May 5;9(3):970-994. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.05.001. eCollection 2024 Sep. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 38770106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the circular RNAs/microRNA/messenger RNA axis in renal cell carcinoma: From gene regulation to metabolism and immunity.iScience. 2025 Mar 11;28(4):112183. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2025.112183. eCollection 2025 Apr 18. iScience. 2025. PMID: 40212586 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

