Design of chimeric GLP-1A using oligomeric bile acids to utilize transporter-mediated endocytosis for oral delivery
- PMID: 37660070
- PMCID: PMC10474648
- DOI: 10.1186/s40824-023-00421-7
Design of chimeric GLP-1A using oligomeric bile acids to utilize transporter-mediated endocytosis for oral delivery
Abstract
Background: Despite the effectiveness of glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist (GLP-1A) in the treatment of diabetes, its large molecular weight and high hydrophilicity result in poor cellular permeability, thus limiting its oral bioavailability. To address this, we developed a chimeric GLP-1A that targets transporter-mediated endocytosis to enhance cellular permeability to GLP-1A by utilizing the transporters available in the intestine, particularly the apical sodium-dependent bile acid transporter (ASBT).
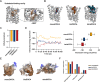
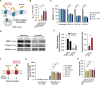
Methods: In silico molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulations were used to investigate the binding interactions of mono-, bis-, and tetra-deoxycholic acid (DOCA) (monoDOCA, bisDOCA, and tetraDOCA) with ASBT. After synthesizing the chimeric GLP-1A-conjugated oligomeric DOCAs (mD-G1A, bD-G1A, and tD-G1A) using a maleimide reaction, in vitro cellular permeability and insulinotropic effects were assessed. Furthermore, in vivo oral absorption in rats and hypoglycemic effect on diabetic db/db mice model were evaluated.
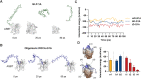
Results: In silico results showed that tetraDOCA had the lowest interaction energy, indicating high binding affinity to ASBT. Insulinotropic effects of GLP-1A-conjugated oligomeric DOCAs were not different from those of GLP-1A-Cys or exenatide. Moreover, bD-G1A and tD-G1A exhibited improved in vitro Caco-2 cellular permeability and showed higher in vivo bioavailability (7.58% and 8.63%) after oral administration. Regarding hypoglycemic effects on db/db mice, tD-G1A (50 μg/kg) lowered the glucose level more than bD-G1A (50 μg/kg) compared with the control (35.5% vs. 26.4%).
Conclusion: GLP-1A was conjugated with oligomeric DOCAs, and the resulting chimeric compound showed the potential not only for glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist activity but also for oral delivery. These findings suggest that oligomeric DOCAs can be used as effective carriers for oral delivery of GLP-1A, offering a promising solution for enhancing its oral bioavailability and improving diabetes treatment.
Keywords: ASBT-mediated endocytosis; Chimeric peptide; In silico molecular docking; Oligomeric bile acids; Oral GLP-1 agonist.
© 2023. The Korean Society for Biomaterials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Coordinated ASBT and EGFR Mechanisms for Optimized Liraglutide Nanoformulation Absorption in the GI Tract.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Mar 23;19:2973-2992. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S442617. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 38544951 Free PMC article.
-
Oligomeric bile acid-mediated oral delivery of low molecular weight heparin.J Control Release. 2014 Feb 10;175:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.12.001. Epub 2013 Dec 12. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24333628
-
Improved peroral delivery of glucagon-like peptide-1 by site-specific biotin modification: design, preparation, and biological evaluation.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008 Mar;68(3):667-75. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2007.07.009. Epub 2007 Aug 2. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2008. PMID: 17904340
-
Bile acid transporter-mediated oral drug delivery.J Control Release. 2020 Nov 10;327:100-116. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.034. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Control Release. 2020. PMID: 32711025 Free PMC article. Review.
-
GLP-1 receptor agonists in the treatment of type 2 diabetes - state-of-the-art.Mol Metab. 2021 Apr;46:101102. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101102. Epub 2020 Oct 14. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33068776 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Preparation and Therapeutic Evaluation of Engineered Semaglutide and Statin-Lipid Conjugate-Based Nanoparticle.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Apr 7;17(4):480. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17040480. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40284475 Free PMC article.
-
Research Progress on the Mechanism of Bile Acids and Their Receptors in Depression.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 24;26(9):4023. doi: 10.3390/ijms26094023. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40362260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Marathe PH, Gao HX, Close KL. American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes 2017. J Diabetes. 2017;9:320–324. - PubMed
-
- Marso SP, Bain SC, Consoli A, Consoli A, Eliaschewitz FG, Jódar E, et al. Semaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:1834–1844. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

