Deploying efficient net batch normalizations (BNs) for grading diabetic retinopathy severity levels from fundus images
- PMID: 37660096
- PMCID: PMC10475020
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41797-9
Deploying efficient net batch normalizations (BNs) for grading diabetic retinopathy severity levels from fundus images
Abstract
Diabetic retinopathy (DR) is one of the main causes of blindness in people around the world. Early diagnosis and treatment of DR can be accomplished by organizing large regular screening programs. Still, it is difficult to spot diabetic retinopathy timely because the situation might not indicate signs in the primary stages of the disease. Due to a drastic increase in diabetic patients, there is an urgent need for efficient diabetic retinopathy detecting systems. Auto-encoders, sparse coding, and limited Boltzmann machines were used as a few past deep learning (DL) techniques and features for the classification of DR. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) have been identified as a promising solution for detecting and classifying DR. We employ the deep learning capabilities of efficient net batch normalization (BNs) pre-trained models to automatically acquire discriminative features from fundus images. However, we successfully achieved F1 scores above 80% on all efficient net BNs in the EYE-PACS dataset (calculated F1 score for DeepDRiD another dataset) and the results are better than previous studies. In this paper, we improved the accuracy and F1 score of the efficient net BNs pre-trained models on the EYE-PACS dataset by applying a Gaussian Smooth filter and data augmentation transforms. Using our proposed technique, we have achieved F1 scores of 84% and 87% for EYE-PACS and DeepDRiD.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
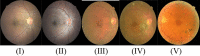
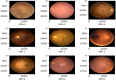
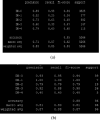
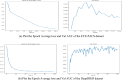
Similar articles
-
Applying supervised contrastive learning for the detection of diabetic retinopathy and its severity levels from fundus images.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Jul;146:105602. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105602. Epub 2022 May 10. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35569335
-
Simple methods for the lesion detection and severity grading of diabetic retinopathy by image processing and transfer learning.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Oct;137:104795. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104795. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34488028
-
A new ultra-wide-field fundus dataset to diabetic retinopathy grading using hybrid preprocessing methods.Comput Biol Med. 2023 May;157:106750. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2023.106750. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Comput Biol Med. 2023. PMID: 36931202
-
Deep learning for diabetic retinopathy detection and classification based on fundus images: A review.Comput Biol Med. 2021 Aug;135:104599. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2021.104599. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Comput Biol Med. 2021. PMID: 34247130 Review.
-
Deep learning based computer-aided diagnosis systems for diabetic retinopathy: A survey.Artif Intell Med. 2019 Aug;99:101701. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Aug 7. Artif Intell Med. 2019. PMID: 31606116 Review.
Cited by
-
Recognition of diabetic retinopathy and macular edema using deep learning.Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024 Sep;62(9):2687-2701. doi: 10.1007/s11517-024-03105-z. Epub 2024 Apr 30. Med Biol Eng Comput. 2024. PMID: 38684593
-
Investigating the relationship between blood metabolites and diabetic retinopathy using two-sample mendelian randomization and in vivo validation.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 3;14(1):22947. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73337-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39362968 Free PMC article.
-
Rheumatoid arthritis and diabetic retinopathy: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jul 26;103(30):e39001. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000039001. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39058858 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li YH, Yeh NN, Chen SJ, Chung YC. Computer-assisted diagnosis for diabetic retinopathy based on fundus images using deep convolutional neural network. Mob. Inf. Syst. 2019;2019(1):2839. doi: 10.1155/2019/6142839. - DOI
-
- da Rocha DA, Ferreira FMF, Peixoto ZMA. Diabetic retinopathy classification using VGG16 neural network. Res. Biomed. Eng. 2022;38(2):761–772. doi: 10.1007/s42600-022-00200-8. - DOI
-
- Saranya P, Prabakaran S. Automatic detection of non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus images using convolution neural network. J. Ambient Intell. Humaniz. Comput. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s12652-020-02518-6. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

