Deciphering migraine pain mechanisms through electrophysiological insights of trigeminal ganglion neurons
- PMID: 37660112
- PMCID: PMC10475091
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41521-7
Deciphering migraine pain mechanisms through electrophysiological insights of trigeminal ganglion neurons
Abstract
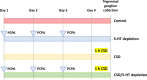
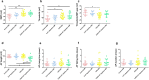
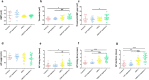
Migraine is a complex neurological disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Despite extensive research, the underlying mechanisms that drive migraine pain and related abnormal sensation symptoms, such as hyperalgesia, allodynia, hyperesthesia, and paresthesia, remain poorly understood. One of the proposed mechanisms is cortical spreading depression (CSD), which is believed to be involved in the regulation of trigeminovascular pathways by sensitizing the pain pathway. Another mechanism is serotonin depletion, which is implicated in many neurological disorders and has been shown to exacerbate CSD-evoked pain at the cortical level. However, the effects of CSD and serotonin depletion on trigeminal ganglion neurons, which play a critical role in pain signal transmission, have not been thoroughly studied. In this study, we aimed to investigate the association between CSD and serotonin depletion with peripheral sensitization processes in nociceptive small-to-medium (SM) and large (L) -sized trigeminal ganglion neurons at the electrophysiological level using rat models. We divided the rats into four groups: the control group, the CSD group, the serotonin depletion group, and the CSD/serotonin depletion group. We induced CSD by placing KCl on a burr hole and serotonin depletion by intraperitoneal injection of PCPA (para-chlorophenoxyacetic acid). We then isolated trigeminal ganglion neurons from all groups and classified them according to size. Using patch-clamp recording, we recorded the excitability parameters and action potential (AP) properties of the collected neurons. Our results showed that in SM-sized trigeminal ganglion neurons, the CSD-SM and CSD/serotonin depletion groups had a higher positive resting membrane potential (RMP) than the control-SM group (p = 0.001 and p = 0.002, respectively, post-hoc Tukey's test). In addition, the gap between RMP and threshold in the CSD-SM group was significantly narrower than in the control-SM group (p = 0.043, post-hoc Tukey's test). For L-sized neurons, we observed prolongation of the AP rising time, AP falling time, and AP duration in neurons affected by CSD (p < 0.05, pairwise comparison test). In conclusion, our study provides new insights into the underlying mechanisms of migraine pain and abnormal somatosensation. CSD and serotonin depletion promote the transmission of pain signals through the peripheral sensitization process of nociceptive small-to-medium-sized trigeminal ganglion neurons, as well as nociceptive and non-nociceptive large-sized trigeminal ganglion neurons.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of high homocysteine levels in migraine pain: An experimental study of the excitability of peripheral meningeal afferents in rats with hyperhomocysteinemia.Headache. 2024 May;64(5):533-546. doi: 10.1111/head.14710. Epub 2024 Apr 22. Headache. 2024. PMID: 38650105
-
Cortical spreading depression induces oxidative stress in the trigeminal nociceptive system.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 3;253:341-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.002. Epub 2013 Sep 11. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24036374
-
Serotonin depletion, cortical spreading depression, and trigeminal nociception.Headache. 2006 Jan;46(1):34-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2006.00310.x. Headache. 2006. PMID: 16412149
-
The science of migraine.J Vestib Res. 2011;21(6):305-14. doi: 10.3233/VES-2012-0433. J Vestib Res. 2011. PMID: 22348935 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neurological mechanisms of migraine: potential of the gap-junction modulator tonabersat in prevention of migraine.Cephalalgia. 2009 Nov;29 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):1-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2982.2009.01976.x. Cephalalgia. 2009. PMID: 19723120 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The TRPA1 Ion Channel Mediates Oxidative Stress-Related Migraine Pathogenesis.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3385. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143385. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
1H-MRS reveals abnormal energy metabolism and excitatory-inhibitory imbalance in a chronic migraine-like state induced by nitroglycerin in mice.J Headache Pain. 2024 Sep 30;25(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s10194-024-01872-6. J Headache Pain. 2024. PMID: 39350002 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

