Tandem NBPF 3mer HORs (Olduvai triplets) in Neanderthal and two novel HOR tandem arrays in human chromosome 1 T2T-CHM13 assembly
- PMID: 37660151
- PMCID: PMC10475015
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-41517-3
Tandem NBPF 3mer HORs (Olduvai triplets) in Neanderthal and two novel HOR tandem arrays in human chromosome 1 T2T-CHM13 assembly
Abstract
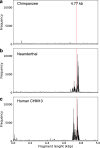
It is known that the ~ 1.6 kb Neuroblastoma BreakPoint Family (NBPF) repeats are human specific and contributing to cognitive capabilities, with increasing frequency in higher order repeat 3mer HORs (Olduvai triplets). From chimpanzee to modern human there is a discontinuous jump from 0 to ~ 50 tandemly organized 3mer HORs. Here we investigate the structure of NBPF 3mer HORs in the Neanderthal genome assembly of Pääbo et al., comparing it to the results obtained for human hg38.p14 chromosome 1. Our findings reveal corresponding NBPF 3mer HOR arrays in Neanderthals with slightly different monomer structures and numbers of HOR copies compared to humans. Additionally, we compute the NBPF 3mer HOR pattern for the complete telomere-to-telomere human genome assembly (T2T-CHM13) by Miga et al., identifying two novel tandem arrays of NBPF 3mer HOR repeats with 5 and 9 NBPF 3mer HOR copies. We hypothesize that these arrays correspond to novel NBPF genes (here referred to as NBPFA1 and NBPFA2). Further improving the quality of the Neanderthal genome using T2T-CHM13 as a reference would be of great interest in determining the presence of such distant novel NBPF genes in the Neanderthal genome and enhancing our understanding of human evolution.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Neuroblastoma Breakpoint Family 3mer Higher Order Repeats/Olduvai Triplet Pattern in the Complete Genome of Human and Nonhuman Primates and Relation to Cognitive Capacity.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 13;15(12):1598. doi: 10.3390/genes15121598. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766865 Free PMC article.
-
Tandemly repeated NBPF HOR copies (Olduvai triplets): Possible impact on human brain evolution.Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Oct 19;6(1):e202101306. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101306. Print 2023 Jan. Life Sci Alliance. 2022. PMID: 36261226 Free PMC article.
-
Global Repeat Map (GRM): Advantageous Method for Discovery of Largest Higher-Order Repeats (HORs) in Neuroblastoma Breakpoint Family (NBPF) Genes, in Hornerin Exon and in Chromosome 21 Centromere.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2021;60:203-234. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-74889-0_8. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 2021. PMID: 34386877
-
Key-string algorithm--novel approach to computational analysis of repetitive sequences in human centromeric DNA.Croat Med J. 2003 Aug;44(4):386-406. Croat Med J. 2003. PMID: 12950141 Review.
-
The X chromosome from telomere to telomere: key achievements and future opportunities.Fac Rev. 2021 Jul 30;10:63. doi: 10.12703/r-01-000001. eCollection 2021. Fac Rev. 2021. PMID: 35088059 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroblastoma Breakpoint Family 3mer Higher Order Repeats/Olduvai Triplet Pattern in the Complete Genome of Human and Nonhuman Primates and Relation to Cognitive Capacity.Genes (Basel). 2024 Dec 13;15(12):1598. doi: 10.3390/genes15121598. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39766865 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient genome monomer higher-order structure annotation and identification using the GRMhor algorithm.Bioinform Adv. 2024 Nov 28;4(1):vbae191. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbae191. eCollection 2024. Bioinform Adv. 2024. PMID: 39659587 Free PMC article.
-
The Applied Genomics Development Strategy by the Croatian Academy of Sciences and Arts paves the way for the future development of applied genomics in Croatia.Croat Med J. 2024 Jun 13;65(3):297-302. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2024.65.297. Croat Med J. 2024. PMID: 38868976 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Assessing genome conservation on pangenome graphs with PanSel.Bioinform Adv. 2025 Mar 5;5(1):vbaf018. doi: 10.1093/bioadv/vbaf018. eCollection 2025. Bioinform Adv. 2025. PMID: 40092526 Free PMC article.
-
Precise identification of cascading alpha satellite higher order repeats in T2T-CHM13 assembly of human chromosome 3.Croat Med J. 2024 Jun 13;65(3):209-219. doi: 10.3325/cmj.2024.65.209. Croat Med J. 2024. PMID: 38868967 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

