MAVS integrates glucose metabolism and RIG-I-like receptor signaling
- PMID: 37660168
- PMCID: PMC10475032
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-41028-9
MAVS integrates glucose metabolism and RIG-I-like receptor signaling
Abstract
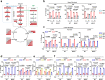
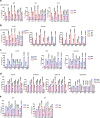
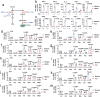
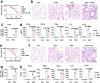
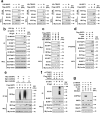
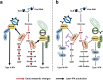
MAVS is an adapter protein involved in RIG-I-like receptor (RLR) signaling in mitochondria, peroxisomes, and mitochondria-associated ER membranes (MAMs). However, the role of MAVS in glucose metabolism and RLR signaling cross-regulation and how these signaling pathways are coordinated among these organelles have not been defined. This study reports that RLR action drives a switch from glycolysis to the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and the hexosamine biosynthesis pathway (HBP) through MAVS. We show that peroxisomal MAVS is responsible for glucose flux shift into PPP and type III interferon (IFN) expression, whereas MAMs-located MAVS is responsible for glucose flux shift into HBP and type I IFN expression. Mechanistically, peroxisomal MAVS interacts with G6PD and the MAVS signalosome forms at peroxisomes by recruiting TNF receptor-associated factor 6 (TRAF6) and interferon regulatory factor 1 (IRF1). By contrast, MAMs-located MAVS interact with glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate transaminase, and the MAVS signalosome forms at MAMs by recruiting TRAF6 and TRAF2. Our findings suggest that MAVS mediates the interaction of RLR signaling and glucose metabolism.
© 2023. Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

